Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) maintains high HIF2A mRNA levels in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 30617181
- PMCID: PMC6416423
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004902
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) maintains high HIF2A mRNA levels in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
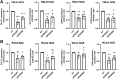
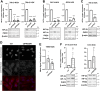
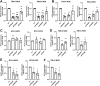
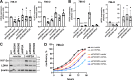
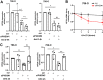
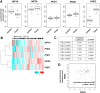
Most clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCCs) have inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein (pVHL), resulting in the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor α-subunits (HIF-α) and their downstream targets. HIF-2α expression is particularly high in ccRCC and is associated with increased ccRCC growth and aggressiveness. In the canonical HIF signaling pathway, HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) suppresses HIF-2α protein by post-translational hydroxylation under sufficient oxygen availability. Here, using immunoblotting and immunofluorescence staining, qRT-PCR, and siRNA-mediated gene silencing, we show that unlike in the canonical pathway, PHD3 silencing in ccRCC cells leads to down-regulation of HIF-2α protein and mRNA. Depletion of other PHD family members had no effect on HIF-2α expression, and PHD3 knockdown in non-RCC cells resulted in the expected increase in HIF-2α protein expression. Accordingly, PHD3 knockdown decreased HIF-2α target gene expression in ccRCC cells and expression was restored upon forced HIF-2α expression. The effect of PHD3 depletion was pinpointed to HIF2A mRNA stability. In line with these in vitro results, a strong positive correlation of PHD3 and HIF2A mRNA expression in ccRCC tumors was detected. Our results suggest that in contrast to the known negative regulation of HIF-2α in most cell types, high PHD3 expression in ccRCC cells maintains elevated HIF-2α expression and that of its target genes, which may enhance kidney cancer aggressiveness.
Keywords: Egl-9 family hypoxia-inducible factor 3 (EGLN3); cancer; cancer biology; ccRCC; hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF); mRNA decay; post-transcriptional regulation; prolyl hydroxylase PHD3; renal cell carcinoma.
© 2019 Miikkulainen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased prolyl hydroxylase 3 mRNA expression in oncocytomas compared with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Int J Biol Markers. 2020 Dec;35(4):80-86. doi: 10.1177/1724600820960478. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int J Biol Markers. 2020. PMID: 33118406
-
Prolyl Hydroxylase 3 Knockdown Accelerates VHL-Mutant Kidney Cancer Growth In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 11;22(6):2849. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062849. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799686 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-independent expression mechanism and novel function of HIF prolyl hydroxylase-3 in renal cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar;140(3):503-13. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1593-7. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24477694 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia, Hypoxia-inducible Transcription Factors, and Renal Cancer.Eur Urol. 2016 Apr;69(4):646-657. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 26298207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hypoxia and Cancer Stem Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Dec;11(6):919-43. doi: 10.1007/s12015-015-9611-y. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 26210994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serial Gene Expression Profiling of Neural Stem Cells Shows Transcriptome Switch by Long-Term Physioxia from Metabolic Adaption to Cell Signaling Profile.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Nov 12;2022:6718640. doi: 10.1155/2022/6718640. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 36411871 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual Antagonism of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Isoforms in Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Disorders.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020 Sep 28;5(9):961-968. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.05.006. eCollection 2020 Sep. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 33015417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Hypoxia-Driven Tumorigenesis: The Interplay of HIF1A, DNA Methylation, and Prolyl Hydroxylases in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 12;25(12):6495. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126495. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928200 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway involvement in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 May;21(5):540. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9972. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33815613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-CATENIN stabilizes HIF2 through lncRNA and inhibits intravenous immunoglobulin immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 8;14:1204907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204907. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37744383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

