A programmed wave of uridylation-primed mRNA degradation is essential for meiotic progression and mammalian spermatogenesis
- PMID: 30617251
- PMCID: PMC6420129
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-018-0128-1
A programmed wave of uridylation-primed mRNA degradation is essential for meiotic progression and mammalian spermatogenesis
Abstract
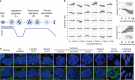
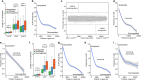
Several developmental stages of spermatogenesis are transcriptionally quiescent which presents major challenges associated with the regulation of gene expression. Here we identify that the zygotene to pachytene transition is not only associated with the resumption of transcription but also a wave of programmed mRNA degradation that is essential for meiotic progression. We explored whether terminal uridydyl transferase 4- (TUT4-) or TUT7-mediated 3' mRNA uridylation contributes to this wave of mRNA degradation during pachynema. Indeed, both TUT4 and TUT7 are expressed throughout most of spermatogenesis, however, loss of either TUT4 or TUT7 does not have any major impact upon spermatogenesis. Combined TUT4 and TUT7 (TUT4/7) deficiency results in embryonic growth defects, while conditional gene targeting revealed an essential role for TUT4/7 in pachytene progression. Loss of TUT4/7 results in the reduction of miRNA, piRNA and mRNA 3' uridylation. Although this reduction does not greatly alter miRNA or piRNA expression, TUT4/7-mediated uridylation is required for the clearance of many zygotene-expressed transcripts in pachytene cells. We find that TUT4/7-regulated transcripts in pachytene spermatocytes are characterized by having long 3' UTRs with length-adjusted enrichment for AU-rich elements. We also observed these features in TUT4/7-regulated maternal transcripts whose dosage was recently shown to be essential for sculpting a functional maternal transcriptome and meiosis. Therefore, mRNA 3' uridylation is a critical determinant of both male and female germline transcriptomes. In conclusion, we have identified a novel requirement for 3' uridylation-programmed zygotene mRNA clearance in pachytene spermatocytes that is essential for male meiotic progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of highly purified mouse spermatogenic cell populations: gene expression signatures switch from meiotic-to postmeiotic-related processes at pachytene stage.BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 19;17:294. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2618-1. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27094866 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA 3' uridylation and poly(A) tail length sculpt the mammalian maternal transcriptome.Nature. 2017 Aug 17;548(7667):347-351. doi: 10.1038/nature23318. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28792939 Free PMC article.
-
Terminal Uridylyltransferases Execute Programmed Clearance of Maternal Transcriptome in Vertebrate Embryos.Mol Cell. 2018 Apr 5;70(1):72-82.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.03.004. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29625039
-
3' RNA Uridylation in Epitranscriptomics, Gene Regulation, and Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jul 13;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00061. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30057901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in spermatogenesis: all RNA pathways lead to healthy sperm.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8049-8071. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04012-4. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34748024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The CNOT4 Subunit of the CCR4-NOT Complex is Involved in mRNA Degradation, Efficient DNA Damage Repair, and XY Chromosome Crossover during Male Germ Cell Meiosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 16;8(10):2003636. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003636. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026442 Free PMC article.
-
The Essential Function of SETDB1 in Homologous Chromosome Pairing and Synapsis during Meiosis.Cell Rep. 2021 Jan 5;34(1):108575. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108575. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33406415 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs: An expanding world with therapeutic promises.Fundam Res. 2023 Apr 6;3(5):676-682. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.03.003. eCollection 2023 Sep. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 38933305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase II pausing is essential during spermatogenesis for appropriate gene expression and completion of meiosis.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 29;15(1):848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45177-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38287033 Free PMC article.
-
Pervasive mRNA uridylation in fission yeast is catalysed by both Cid1 and Cid16 terminal uridyltransferases.PLoS One. 2023 May 23;18(5):e0285576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285576. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37220133 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

