A phase 1, first-in-human study of 18F-GP1 positron emission tomography for imaging acute arterial thrombosis
- PMID: 30617563
- PMCID: PMC6323046
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-018-0471-8
A phase 1, first-in-human study of 18F-GP1 positron emission tomography for imaging acute arterial thrombosis
Abstract
Background: 18F-GP1 is a novel positron emission tomography (PET) tracer that targets glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors on activated platelets. The study objective was to explore the feasibility of directly imaging acute arterial thrombosis (AAT) with 18F-GP1 PET/computed tomography (PET/CT) and to quantitatively assess 18F-GP1 uptake. Safety, biodistribution, pharmacokinetics and metabolism were also evaluated.
Methods: Adult patients who had signs or symptoms of AAT or had recently undergone arterial intervention or surgery within 14 days prior to 18F-GP1 PET/CT were eligible for inclusion. The AAT focus was demonstrated by conventional imaging within the 5 days prior to 18F-GP1 administration. Whole-body dynamic 18F-GP1 PET/CT images were acquired for up to 140 min after injection of 250 MBq of 18F-GP1. Venous plasma samples were analysed to determine 18F-GP1 clearance and metabolite formation.
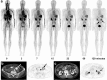
Results: Among the ten eligible patients assessed, underlying diseases were abdominal aortic aneurysm with endovascular repair (n = 6), bypass surgery and stent placement (n = 1), endarterectomy (n = 1), arterial dissection (n = 1) and acute cerebral infarction (n = 1). 18F-GP1 administration and PET/CT procedures were well tolerated, with no drug-related adverse events. All patients showed high initial 18F-GP1 uptake in the spleen, kidney and blood pool, followed by rapid clearance. Unmetabolised plasma 18F-GP1 levels peaked at 4 min post-injection and decreased over time until 120 min. The overall image quality was sufficient for diagnosis in all patients and AAT foci were detected in all participants. The 18F-GP1 uptake in AAT foci remained constant from 7 min after injection and began to separate from the blood pool after 20 min. The median standardised uptake value of AAT was 5.0 (range 2.4-7.9) at 120 min post-injection. The median ratio of standardised uptake value of AAT foci to the mean blood pool activity was 3.4 (range 2.0-6.3) at 120 min.
Conclusions: 18F-GP1 is a safe and promising novel PET tracer for imaging AAT with a favourable biodistribution and pharmacokinetic profile.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02864810 , Registered August 3, 2016.
Keywords: 18F-GP1; Arterial thrombosis; Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor; Platelet activation; Positron emission tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea and the Asan Medical Center Institutional Review Board (2016-0138). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
DHM has received research grants from Life Molecular Imaging GmbH (formerly Piramal Imaging GmbH, Berlin, Germany). NK, MB and AWS are employees of Life Molecular Imaging GmbH, formerly Piramal Imaging GmbH, Berlin, Germany. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goff DC, Jr, Lloyd-Jones DM, Bennett G, Coady S, D'Agostino RB, Gibbons R, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129:S49–S73. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000437741.48606.98. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

