A Review of Iodine Status of Women of Reproductive Age in the USA
- PMID: 30617900
- PMCID: PMC6373336
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-018-1606-5
A Review of Iodine Status of Women of Reproductive Age in the USA
Abstract
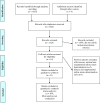
Iodine, an essential micronutrient, is required to produce thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) comprise a range of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes, with the most significant irreversible effect resulting from neurodevelopmental deficits in fetal brain caused by deficient iodine status during early pregnancy. The objective of this scoping review was to summarize the studies that assessed iodine status of women of reproductive age in the USA. A systematic review of literature using the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) statement was conducted. PubMed, Medline, CINAHL, EMBASE, EBSCOHost, Cochrane, ERIC, Google Scholar, and Web of Science databases were searched, 1652 records were identified. One thousand six hundred forty-one records that did not satisfy the inclusion/exclusion criteria and quality review were excluded, and 11 peer-reviewed articles were determined to be eligible for this scoping review. Despite the USA being considered iodine sufficient for the general population, the US dietary iodine intakes have decreased drastically since the 1970s, with iodine deficiency reemerging in vulnerable groups such as women of reproductive age. Although data to conduct a scoping review of iodine status among women of reproductive age in the USA was scarce, majority of the articles reviewed demonstrate emergent iodine deficiency in this population of women of reproductive age, indicating alarm for a public health concern needing immediate attention.
Keywords: Iodine; Iodine deficiency; Iodine status; Thyroid; Urinary iodine; Women of reproductive age.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Similar articles
-
Insufficient iodine nutrition status and the risk of pre-eclampsia: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2019 May 24;9(5):e025573. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025573. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31129578 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Thyroglobulin Concentration and Maternal Iodine Status During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Thyroid. 2020 May;30(5):767-779. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0712. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Thyroid. 2020. PMID: 31910106
-
Effects of mandatory salt iodization on breast milk, urinary iodine concentrations, and thyroid hormones: is iodine deficiency still a continuing problem?J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Apr;42(4):411-418. doi: 10.1007/s40618-018-0930-0. Epub 2018 Aug 11. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019. PMID: 30099723
-
Do maternal urinary iodine concentration or thyroid hormones within the normal range during pregnancy affect growth parameters at birth? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Rev. 2020 Sep 1;78(9):747-763. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz105. Nutr Rev. 2020. PMID: 31923312
Cited by
-
Salt-Containing Recipes in Popular Magazines with the Highest Circulation in the United States Do Not Specify Iodized Salt in the Ingredient List.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 5;20(5):4595. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054595. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36901606 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine adequacy in reproductive age and pregnant women living in the Western region of Saudi Arabia.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 Jun 22;20(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-03057-w. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 32571259 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine Status of Women and Infants in Russia: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 11;17(22):8346. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228346. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33187335 Free PMC article.
-
Vegans, Vegetarians and Pescatarians Are at Risk of Iodine Deficiency in Norway.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 20;12(11):3555. doi: 10.3390/nu12113555. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33233534 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine Deficiency, Maternal Hypothyroxinemia and Endocrine Disrupters Affecting Fetal Brain Development: A Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2023 May 9;15(10):2249. doi: 10.3390/nu15102249. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venturi S, Donati F, Venturi A, Venturi M, Grossi L, Guidi A. Role of iodine in evolution and carcinogenesis of thyroid, breast and stomach. Adv Clin Pathol. 2000;4(1):11–17. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine, Academy of Sciences. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin a, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium and zinc. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources