Genetic effects on promoter usage are highly context-specific and contribute to complex traits
- PMID: 30618377
- PMCID: PMC6349408
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.41673
Genetic effects on promoter usage are highly context-specific and contribute to complex traits
Abstract
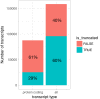
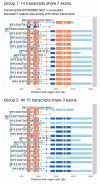
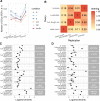
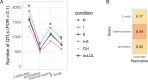
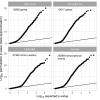
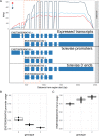
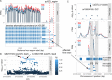
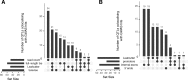
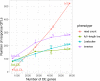
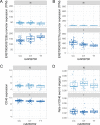
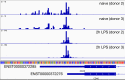
Genetic variants regulating RNA splicing and transcript usage have been implicated in both common and rare diseases. Although transcript usage quantitative trait loci (tuQTLs) have been mapped across multiple cell types and contexts, it is challenging to distinguish between the main molecular mechanisms controlling transcript usage: promoter choice, splicing and 3' end choice. Here, we analysed RNA-seq data from human macrophages exposed to three inflammatory and one metabolic stimulus. In addition to conventional gene-level and transcript-level analyses, we also directly quantified promoter usage, splicing and 3' end usage. We found that promoters, splicing and 3' ends were predominantly controlled by independent genetic variants enriched in distinct genomic features. Promoter usage QTLs were also 50% more likely to be context-specific than other tuQTLs and constituted 25% of the transcript-level colocalisations with complex traits. Thus, promoter usage might be an underappreciated molecular mechanism mediating complex trait associations in a context-specific manner.
Keywords: RNA-seq; computational biology; genetics; genomics; human; macrophages; splicing; systems biology; transcription.
© 2019, Alasoo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KA, JR, JD, DP, DG No competing interests declared, DF Since October 2015, Daniel F Freitag has been a full-time employee of Bayer AG, Germany
Figures









References
-
- Alasoo K, Martinez FO, Hale C, Gordon S, Powrie F, Dougan G, Mukhopadhyay S, Gaffney DJ. Transcriptional profiling of macrophages derived from monocytes and iPS cells identifies a conserved response to LPS and novel alternative transcription. Scientific Reports. 2015;5:12524. doi: 10.1038/srep12524. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alasoo K. wiggleplotr: Make read coverage plots from BigWig files. Bioconductor 2017
-
- Alasoo K, Rodrigues J, Mukhopadhyay S, Knights AJ, Mann AL, Kundu K, Hale C, Dougan G, Gaffney DJ, HIPSCI Consortium Shared genetic effects on chromatin and gene expression indicate a role for enhancer priming in immune response. Nature Genetics. 2018;50:424–431. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0046-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alasoo K. txrevise. 5532b3dGithub. 2018a https://github.com/kauralasoo/txrevise
-
- Alasoo K. macrophage-tuQTLs. 5fafd68Github. 2018b https://github.com/kauralasoo/macrophage-tuQTLs
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

