Spatiotemporal Structure and Dynamics of Spontaneous Oscillatory Synchrony in the Vagal Complex
- PMID: 30618595
- PMCID: PMC6305462
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00978
Spatiotemporal Structure and Dynamics of Spontaneous Oscillatory Synchrony in the Vagal Complex
Abstract
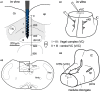
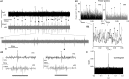
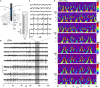
Fundamental structure and dynamics of spontaneous neuronal activities without apparent peripheral inputs were analyzed in the vagal complex (VC), whose activities had been generally thought to be produced almost passively to peripheral cues. The analysis included the caudal nucleus of the tractus solitarius-a main gateway for viscerosensory peripheral afferents and involved dynamically and critically in cardiorespiratory brainstem networks. In the present study, a possibility of self-organized brain activity was addressed in the VC. While VC neurons exhibited sparse firing in anesthetized rats and in in vitro preparations, we identified peculiar features of the emergent electrical population activity: (1) Spontaneous neuronal activity, in most cases, comprised both respiration and cardiac cycle components. (2) Population potentials of polyphasic high amplitudes reaching several millivolts emerged in synchrony with the inspiratory phase of respiratory cycles and exhibited several other characteristic temporal dynamics. (3) The spatiotemporal dynamics of local field potentials (LFPs), recorded simultaneously over multiple sites, were characterized by a stochastic emergence of high-amplitude synchrony. By adjusting amplitude and frequency (phase) over both space and time, the traveling synchrony exhibited varied degrees of coherence and power with a fluctuating balance between mutual oscillators of respiratory and cardiac frequency ranges. Full-fledged large-scale oscillatory synchrony over a wide region of the VC emerged after achieving a maximal stable balance between the two oscillators. Distinct somatic (respiratory; ~1 Hz) and visceral (autonomic; ~5 Hz) oscillators seemed to exist and communicate co-operatively in the brainstem network. Fluctuating oscillatory coupling may reflect varied degrees of synchrony influenced by the varied amplitude and frequency of neuronal activity in the VC. Intranuclear micro-, intrabulbar meso-, and wide-ranging macro-circuits involving the VC are likely to form nested networks and strategically interact to maintain a malleable whole-body homeostasis. These two brainstem oscillators could orchestrate neuronal activities of the VC, and other neuronal groups, through a phase-phase coupling mechanism to perform specific physiological functions.
Keywords: brain wave; electrical activity; emergence; oscillator; self-organization; viscerosensory.
Figures






References
-
- Buzsaki G. (2006). Rhythms of the Brain. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, Inc; 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195301069.001.0001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

