Cardioprotection of Ginkgolide B on Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Inflammatory Injury via Regulation of A20-NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 30619251
- PMCID: PMC6299132
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02844
Cardioprotection of Ginkgolide B on Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Inflammatory Injury via Regulation of A20-NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
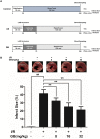
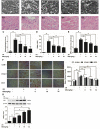
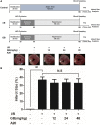
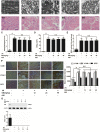
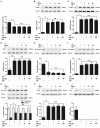
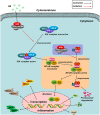
Inflammation urges most of the characteristics of plaques involved in the pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MI/RI). In addition, inflammatory signaling pathways not only mediate the properties of plaques that precipitate ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) but also influence the clinical consequences of the post-infarction remodeling and heart failure. Here, we studied whether Ginkgolide B (GB), an effective anti-inflammatory monomer, improved MI/RI via suppression of inflammation. Left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery induced ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) of rats or A20 silencing mice, as well as hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) induced damages of primary cultured rat neonatal ventricular myocytes or A20 silencing ventricular myocytes, respectively, served as MI/RI model in vivo and in vitro to discuss the anti-I/R injury properties of GB. We found that GB significantly alleviated the symptoms of MI/RI evidently by reducing infarct size, preventing ultrastructural changes of myocardium, depressing Polymorphonuclears (PMNs) infiltration, lessening histopathological damage and suppressing the excessive inflammation. Further study demonstrated that GB remarkably inhibited NF-κB p65 subunit translocation, IκB-α phosphorylation, IKK-β activity, as well as the downstream inflammatory cytokines and proteins expressions via zinc finger protein A20. In conclusion, GB could alleviate MI/RI-induced inflammatory response through A20-NF-κB signal pathway, which may give us new insights into the preventive strategies for MI/RI disease.
Keywords: A20; Ginkgolide B; Inflammation; Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; NF-κB.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ginkgolide C Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Inflammatory Injury via Inhibition of CD40-NF-κB Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Feb 21;9:109. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00109. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29515442 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide C attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory impairments by suppressing CD40/NF-κB pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Aug 10;312:116537. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116537. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37094696
-
Inhibition of NF-κB activation is associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012 Nov 20;47(4):652-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2012.07.016. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 22850444
-
Communication Regarding the Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion and Cognitive Impairment: A Narrative Literature Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(4):1545-1570. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230886. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38277294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between T lymphocytes and macrophages in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Aug;479(8):1925-1936. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04822-z. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37540399 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin elicits protective effects on OGD/R‑insulted H9c2 cells by activating PGC‑1α/Nrf2 signaling.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1294-1304. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4514. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323734 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective cohort study on serum A20 as a prognostic biomarker of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(5):360-366. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.079. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37908792 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of hypoxia-related genes in diagnosis and immune infiltration in acute myocardial infarction: based on bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Aug 21;11:1448705. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1448705. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39234566 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B Alleviates Learning and Memory Impairment in Rats With Vascular Dementia by Reducing Neuroinflammation via Regulating NF-κB Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 17;12:676392. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.676392. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34220511 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B alleviates the inflammatory response and attenuates the activation of LPS-induced BV2 cells in vitro and in vivo.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):586. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10018. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33850558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Enesa K, Evans P. The biology of A20-like molecules. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2014) 809:33–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

