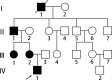
GJB6 mutation A88V for hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in a Chinese family
- PMID: 30620052
- PMCID: PMC6905398
- DOI: 10.1111/ijd.14341
GJB6 mutation A88V for hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in a Chinese family
Figures



References
-
- Zhang XJ, Chen JJ, Yang S, et al A mutation in the connexin 30 gene in Chinese Han patients with hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. J Dermatol Sci 2003; 32: 11–17. - PubMed
-
- Lamartine J, Munhoz Essenfelder G, Kibar Z, et al Mutations in GJB6 cause hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 142–144. - PubMed
-
- Smith FJ, Morley SM, McLean WH. A novel connexin 30 mutation in Clouston syndrome. J Invest Dermatol 2002; 118: 530–532. - PubMed
-
- Baris HN, Zlotogorski A, Peretz‐Amit G, et al A novel GJB6 missense mutation in hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia 2 (Clouston syndrome) broadens its genotypic basis. Br J Dermatol 2008; 159: 1373–1376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

