Attachment strength and on-farm die-off rate of Escherichia coli on watermelon surfaces
- PMID: 30620744
- PMCID: PMC6324798
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210115
Attachment strength and on-farm die-off rate of Escherichia coli on watermelon surfaces
Abstract
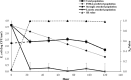
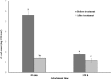
Pre-harvest contamination of produce has been a major food safety focus. Insight into the behavior of enteric pathogens on produce in pre-harvest conditions will aid in developing pre-harvest and post-harvest risk management strategies. In this study, the attachment strength (SR) and die-off rate of E. coli on the surface of watermelon fruits and the efficacy of aqueous chlorine treatment against strongly attached E. coli population were investigated. Watermelon seedlings were transplanted into eighteen plots. Prior to harvesting, a cocktail of generic E. coli (ATCC 23716, 25922 and 11775) was inoculated on the surface of the watermelon fruits (n = 162) and the attachment strength (SR) values and the daily die-off rates were examined up to 6 days by attachment assay. After 120 h, watermelon samples were treated with aqueous chlorine (150 ppm free chlorine for 3 min). The SR value of the E. coli cells on watermelon surfaces significantly increased (P<0.05) from 0.04 to 0.99 in the first 24 h, which was primarily due to the decrease in loosely attached population, given that the population of strongly attached cells was constant. Thereafter, there was no significant change in SR values, up to 120 h. The daily die-off rate of E. coli ranged from -0.12 to 1.3 log CFU/cm2. The chlorine treatment reduced the E. coli level by 4.2 log CFU/cm2 (initial level 5.6 log CFU/cm2) and 0.62 log CFU/cm2 (initial level 1.8 log CFU/cm2), on the watermelons that had an attachment time of 30 min and 120 h respectively. Overall, our findings revealed that the population of E. coli on watermelon surfaces declined over time in an agricultural environment. Microbial contamination during pre-harvest stages may promote the formation of strongly attached cells on the produce surfaces, which could influence the efficacy of post-harvest washing and sanitation techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Crowe SJ, Mahon BE, Vieira AR, Gould LH. Vital signs: multistate foodborne outbreaks-United States, 2010–2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(43):1221–5. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6443a4.htm - PubMed
-
- Graça A, Esteves E, Nunes C, Abadias M, Quintas C. Microbiological quality and safety of minimally processed fruits in the marketplace of southern Portugal. Food Control. 2017;73:775–83.
-
- Scharff RL. Health-related costs from foodborne illness in the United States. The Produce Safety Project at Georgetown University. 2010. Available from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.172.4518&rep=re... [cited 2018].
-
- Ackers M-L, Mahon BE, Leahy E, Goode B, Damrow T, Hayes PS, et al. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 infections associated with leaf lettuce consumption. J. Infect. Dis. 1998;177(6):1588–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

