Costs of clinical trials with anticancer biological agents in an Oncologic Italian Cancer Center using the activity-based costing methodology
- PMID: 30620767
- PMCID: PMC6324822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210330
Costs of clinical trials with anticancer biological agents in an Oncologic Italian Cancer Center using the activity-based costing methodology
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to assess the estimated "per patient" total cost for a single Oncologic Italian Cancer Center participating in a multicenter clinical trial with new anticancer biological agents using the activity-based costing (ABC) methodology.
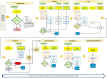
Methodology: Nine randomized phase 3 clinical trials employing biological agents at the National Cancer Institute of Napoli, Italy, were analyzed to indentify "per patient" costs of each trial, according to the ABC methodology. The average consumption of resources for a patient completing the entire planned treatment was estimated for each trial. Through interviews of the personnel (doctors, nurses and technicians) and by analyses of the clinical trials protocols, the main activities of the 9 clinical trials were identified and, for each trial, the complete health care pathway of the patients and the treatment programmes were minutely reconstructed. Drug costs were not included because provided by Sponsors.
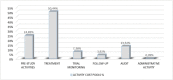
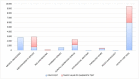
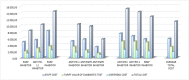
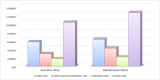
Principal findings: The average costs of the pre-study, treatment, monitoring, follow-up, audit, and administrative activities accounted for 2.357, 4.783, 700, 372, 1.263, and 9 Euro, respectively. The average total cost estimated for all "per patient" activities, including overhead costs, was 11.379 Euro. Staff costs accounted for € 5.988, while costs of diagnostic test accounted for 3.494 Euro. Clinical trials with immunotherapeutic drugs accounted for higher costs (+601 Euro as oncological staff costs, +1.318 Euro as intermediate services cost and +384 Euro as overheads).
Conclusions: The average total cost estimated for all "per patient" activities of a clinical trial with new anticancer biological agents was 11.379 Euro using the ABC methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Jones B, Eliasziw M, Eigl BJ, Syme R. A Comparison of Incremental Costs of Breast Cancer Clinical Trials to Standard of Care. Journal of Clinical Trials. 2015; 5:216.
-
- Lievens Y, Van Den Bogaert W, Kesteloot K. Activity-Based Costing: a Practical Model for Cost Calculation in Radiotherapy. Int. Journal Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 2003; 57(2):522–35. - PubMed
-
- Ridderstolpe L, Johansson A, Skau T, Rutberg H, Ahlfeldt H. Clinical Process Analysis and Activity-Based Costing at a Heart Center. Journal of Medical Systems. 2002; 26(4):309–22. - PubMed
-
- Grandlich C. Using activity-based costing in surgery. AORN Journal. 2004; 79(1):189–92. - PubMed
-
- Udpa S. Activity Based Costing for hospitals. Health Care Manage Review.1996; 21:83–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

