Behavioral validation of a wireless low-power neurostimulation technology in a conditioned place preference task
- PMID: 30620935
- PMCID: PMC6765399
- DOI: 10.1088/1741-2552/aafc72
Behavioral validation of a wireless low-power neurostimulation technology in a conditioned place preference task
Abstract
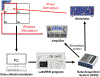
Objective: Neurostimulation technologies are important for studying neural circuits and the connections that underlie neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, current methods come with limitations such as the restraint on movement imposed by the wires delivering stimulation. The objective of this study was to assess whether the e-Particle (EP), a novel wireless neurostimulator, could sufficiently stimulate the brain to modify behavior without these limitations.
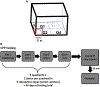
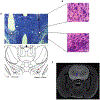
Approach: Rats were implanted with the EP and a commercially available stimulating electrode. Animals received rewarding brain stimulation, and performance in a conditioned place preference (CPP) task was measured. To ensure stimulation-induced neuronal activation, immediate early gene c-fos expression was also measured.
Main results: The EP was validated in a commonly used CPP task by demonstrating that (1) wireless stimulation via the EP induced preference behavior that was comparable to that induced by standard wired electrodes and (2) neuronal activation was observed in projection targets of the stimulation site.
Significance: The EP may help achieve a better understanding of existing brain stimulation methods while overcoming their limitations. Validation of the EP in a behavioral model suggests that the benefits of this technology may extend to other areas of animal research and potentially to human clinical applications.
Figures




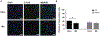
Similar articles
-
Miniature electroparticle-cuff for wireless peripheral neuromodulation.J Neural Eng. 2019 Aug;16(4):046002. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab1c36. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Neural Eng. 2019. PMID: 31018187
-
Miniaturised Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Neurostimulation: A Review.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2020 Dec;14(6):1160-1178. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2020.3038599. Epub 2020 Dec 31. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2020. PMID: 33201828 Review.
-
Integrated wireless fast-scan cyclic voltammetry recording and electrical stimulation for reward-predictive learning in awake, freely moving rats.J Neural Eng. 2013 Aug;10(4):046007. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/4/046007. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Neural Eng. 2013. PMID: 23770892
-
Peripheral Neurostimulation with a Microsize Wireless Stimulator.Prog Neurol Surg. 2015;29:168-91. doi: 10.1159/000434670. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Prog Neurol Surg. 2015. PMID: 26394030 Review.
-
A low-cost multichannel wireless neural stimulation system for freely roaming animals.J Neural Eng. 2013 Dec;10(6):066010. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/10/6/066010. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Neural Eng. 2013. PMID: 24162159
Cited by
-
Microenvironment-responsive electrocution of tumor and bacteria by implants modified with degenerate semiconductor film.Bioact Mater. 2022 Jun 24;20:472-488. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.06.004. eCollection 2023 Feb. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35800406 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical Implants with Charge-Transfer Monitoring and Regulating Abilities.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Aug;8(16):e2004393. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004393. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34166584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wireless Power Delivery Techniques for Miniature Implantable Bioelectronics.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Sep;10(17):e2100664. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202100664. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 34114368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetoelectric Materials for Miniature, Wireless Neural Stimulation at Therapeutic Frequencies.Neuron. 2020 Aug 19;107(4):631-643.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.05.019. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32516574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benabid AL, Pollak P, Louveau A, Henry S and de Rougemont J 1987. Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson disease Appl. Neurophysiol 50 344–6 - PubMed
-
- Bewernick BH, Kayser S, Gippert SM, Switala C, Coenen VA and Schlaepfer TE 2017. Deep brain stimulation to the medial forebrain bundle for depression-long-term outcomes and a novel data analysis strategy Brain Stimul 10 664–71 - PubMed
-
- Camprodon JA, Rauch SL, Greenberg BD and Dougherty DD 2016. Psychiatric Neurotherapeutics: Contemporary Surgical and Device-Based Treatments (New York, NY: Humana Press; )
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
