A Literature Review of Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer in Japan
- PMID: 30621278
- PMCID: PMC6352078
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8010048
A Literature Review of Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer in Japan
Abstract
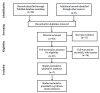
Aim: Patients of proton beam therapy (PBT) for prostate cancer had been continuously growing in number due to its promising characteristics of high dose distribution in the tumor target and a sharp distal fall-off. Considering the large number of proton beam facilities in Japan, the further increase of patients undergoing this treatment is due to the emendations by Japanese National Health Insurance (NHI) and the development of medical equipment and technology, it is necessary to know what kind of research and advancements has been done on proton therapy for prostate cancer in the country. For these reasons, this literature review was conducted. The aim of this review is to identify and discuss research studies of proton beam therapy for prostate cancer in Japan. These include observational, interventional, and secondary data analysis of published articles. Method: A literature review on published works related to proton beam therapy for prostate cancer in Japan was conducted using articles that were gathered in the PubMed database of June 2018. We went through abstracts and manuscripts written in English with the keywords 'proton beam therapy', 'prostate cancer', and 'Japan'. Results: A total of 23 articles were included. Fourteen articles were observational studies, most of which focused on the adverse effects of Proton Beam Therapy (PBT). Seven articles were interventional studies related on treatment planning, equipment parts, as well as target positioning. Two were secondary data analysis. The included studies were published in 13 different journals by different institutions using various equipment. Conclusion: Despite the favorable results of proton beam therapy, future research should include more patients and longer follow-up schedules to clarify the definitive role of PBT, yet, up to recent retrospective studies, included in this paper, concluded that PBT can be a suitable treatment option for localized prostate cancer. In addition, interventional studies were conducted by several institutions to further embellish proton therapy.
Keywords: Japan; literature review; prostate cancer; proton therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Particle beam therapy for pelvic recurrence of colorectal cancer: a registry data analysis in Japan and a systematic review.J Radiat Res. 2023 Jun 16;64(Supplement_1):i25-i33. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrad024. J Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37117038 Free PMC article.
-
Proton beam therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2013 Apr-Jun;3(2):e87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24674325 Review.
-
Proton beam therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer.Cancer J. 2014 Nov-Dec;20(6):415-20. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000083. Cancer J. 2014. PMID: 25415688 Review.
-
Model-based cost-effectiveness analysis of external beam radiation therapy for the treatment of localized prostate cancer: a systematic review.Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2019 May 21;17:10. doi: 10.1186/s12962-019-0178-3. eCollection 2019. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2019. PMID: 31139024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Patterns of Care and Referral Between Proton and Photon Therapy.Int J Part Ther. 2024 Apr 22;11:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpt.2023.10.001. eCollection 2024 Mar. Int J Part Ther. 2024. PMID: 38757072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Reasearch UK World Cancer Statistics. [(accessed on 21 June 2018)]; Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/w....
-
- Molina R.A.C., Navarro F.B.G. Cancer de Prostata. SciELO. 2016;2:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Statistics in Japan; Table Download. [(accessed on 14 October 2018)]; Available online: https://ganjoho.jp/en/professional/statistics/table_download.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources