Investigation of the structural requirements for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor positive and negative allosteric modulators based on 2-naphthoic acid
- PMID: 30622023
- PMCID: PMC7043280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.12.054
Investigation of the structural requirements for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor positive and negative allosteric modulators based on 2-naphthoic acid
Abstract
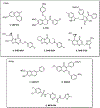
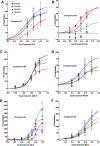
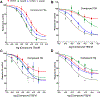
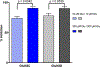
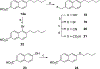
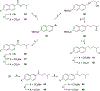
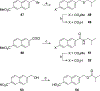
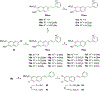
The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), a ligand-gated ion channel activated by L-glutamate and glycine, plays a major role in the synaptic plasticity underlying learning and memory. NMDARs are involved in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease and NMDAR hypofunction is implicated in schizophrenia. Herein we describe structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies on 2-naphthoic acid derivatives to investigate structural requirements for positive and negative allosteric modulation of NMDARs. These studies identified compounds such as UBP684 (14b), which act as pan potentiators by enhancing NMDAR currents in diheteromeric NMDAR tetramers containing GluN1 and GluN2A-D subunits. 14b and derivatives thereof are useful tools to study synaptic function and have potential as leads for the development of drugs to treat schizophrenia and disorders that lead to a loss of cognitive function. In addition, SAR studies have identified a series of styryl substituted compounds with partial NAM activity and a preference for inhibition of GluN2D versus the other GluN2 subunits. In particular, the 3-and 2-nitrostyryl derivatives UBP783 (79i) and UBP792 (79h) had IC50s of 1.4 μM and 2.9 μM, respectively, for inhibition of GluN2D but showed only 70-80% maximal inhibition. GluN2D has been shown to play a role in excessive pain transmission due to nerve injury and potentially in neurodegenerative disorders. Partial GluN2D inhibitors may be leads for the development of drugs to treat these disorders without the adverse effects observed with full NMDAR antagonists.
Keywords: 2-Naphthoic acid; GluN2; N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NMDA; Negative allosteric modulator; Positive allosteric modulator.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
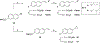

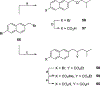

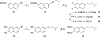
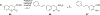
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological characterization of a novel negative allosteric modulator of NMDA receptors, UBP792.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Dec 15;201:108818. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108818. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34610288
-
Mechanism and properties of positive allosteric modulation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors by 6-alkyl 2-naphthoic acid derivatives.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28709671 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Negative Allosteric Modulator Selective for GluN2C/2D-Containing NMDA Receptors Inhibits Synaptic Transmission in Hippocampal Interneurons.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Feb 21;9(2):306-319. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00329. Epub 2017 Nov 2. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29043770 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing NMDA Receptor Function: Recent Progress on Allosteric Modulators.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:2875904. doi: 10.1155/2017/2875904. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28163934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of GluN2A NMDA receptor positive allosteric modulators: Recent advances and perspectives.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Jul 1;124:118194. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2025.118194. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40239379 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of STP, LTP and LTD by structurally diverse NMDA receptor subunit-specific positive allosteric modulators.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Jan 1;202:108840. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108840. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 34678377 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptor Antagonists: Emerging Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications in Neurological Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 15;17(5):639. doi: 10.3390/ph17050639. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-Pot Formal Carboradiofluorination of Alkenes: A Toolkit for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Probe Development.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Sep 6;145(35):19265-19273. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c04548. Epub 2023 Aug 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37625118 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Oct;73(4):298-487. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000131. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progresses in GluN2A-containing NMDA Receptors and their Selective Regulators.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):139-153. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01185-1. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 34978648 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Watkins JC; Jane DE The glutamate story. Br. J. Pharmacol 2006, 147, S100–S108. - PMC - PubMed
- Kew JNC; Kemp JA Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor structure and pharmacology. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 4–29. - PubMed
- Traynelis SF; Wollmuth LP; McBain CJ; Menniti FS; Vance KM; Ogden KK; Hansen KB; Yuan H; Myers SJ; Dingledine R Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacological Reviews 2010, 62, 405–496. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Monaghan DT; Jane DE (2008) Pharmacology of the NMDA receptor In Biology of the NMDA receptor. Ed. Antonius VanDongen, Taylor and Francis, London, UK: pp 257–282.
-
- Collingridge GL Synaptic plasticity. The role of NMDA receptors in learning and memory. Nature 1987, 330, 604–605. - PubMed
-
- Kalia LV; Kalia SK; Salter MW NMDA receptors in clinical neurology: excitatory times ahead. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 742–755. - PMC - PubMed
- Hizue M; Pang CH, Yokoyama M Involvement of N-methyl-D-aspartate-type glutamate receptor epsilon I and epsilon 4 subunits in tonic inflammatory pain and neuropathic pain. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1667–1670. - PubMed
- Sanacora G; Zarate CA; Krystal JH; Manji HK. Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov 2008, 7, 426–437. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

