Artificial light-driven ion pump for photoelectric energy conversion
- PMID: 30622279
- PMCID: PMC6325115
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-08029-5
Artificial light-driven ion pump for photoelectric energy conversion
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Artificial light-driven ion pump for photoelectric energy conversion.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 14;10(1):843. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08815-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30765697 Free PMC article.
Abstract
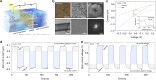
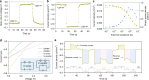
Biological light-driven ion pumps move ions against a concentration gradient to create a membrane potential, thus converting sunlight energy directly into an osmotic potential. Here, we describe an artificial light-driven ion pump system in which a carbon nitride nanotube membrane can drive ions thermodynamically uphill against an up to 5000-fold concentration gradient by illumination. The separation of electrons and holes in the membrane under illumination results in a transmembrane potential which is thought to be the foundation for the pumping phenomenon. When used for harvesting solar energy, a sustained open circuit voltage of 550 mV and a current density of 2.4 μA/cm2 can reliably be generated, which can be further scaled up through series and parallel circuits of multiple membranes. The ion transport based photovoltaic system proposed here offers a roadmap for the development of devices by using simple, cheap, and stable polymeric carbon nitride.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- El-Sayed MA. On the molecular mechanisms of the solar to electric energy conversion by the other photosynthetic system in nature, bacteriorhodopsin. Acc. Chem. Res. 1992;25:279–286. doi: 10.1021/ar00019a002. - DOI
-
- Tributsch H. Light driven proton pumps. Ionics. 2000;6:161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF02374062. - DOI
-
- Steinberg-Yfrach G, et al. Conversion of light energy to proton potential in liposomes by artificial photosynthetic reaction centres. Nature. 1997;385:239. doi: 10.1038/385239a0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

