Ethanol Extract of Cudrania tricuspidata Leaf Ameliorates Hyperuricemia in Mice via Inhibition of Hepatic and Serum Xanthine Oxidase Activity
- PMID: 30622611
- PMCID: PMC6304516
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8037925
Ethanol Extract of Cudrania tricuspidata Leaf Ameliorates Hyperuricemia in Mice via Inhibition of Hepatic and Serum Xanthine Oxidase Activity
Abstract
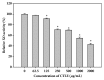
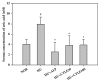
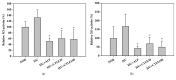
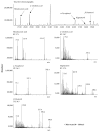
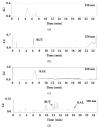
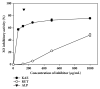
Cudrania tricuspidata Bureau (Moraceae) (CT) is a dietary and medicinal plant distributed widely in Northeast Asia. There have been no studies on the effect of CT and/or its active constituents on in vivo xanthine oxidase (XO) activity, hyperuricemia, and gout. The aim of this study was to investigate XO inhibitory and antihyperuricemic effects of the ethanol extract of CT leaf (CTLE) and its active constituents in vitro and in vivo. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analyses were used to determine a chemical profile of CTLE. XO inhibitory and antihyperuricemic effects of CTLE given orally (30 and 100 mg/kg per day for 1 week) were examined in potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemic ICR mice. CTLE exhibited XO inhibitory activity in vitro with an IC50 of 368.2 μg/mL, significantly reduced serum uric acid levels by approximately 2-fold (7.9 nM in normal mice; 3.8 nM in 30 mg/kg CTLE; 3.9 nM in 100 mg/kg CTLE), and significantly alleviated hyperuricemia by reducing hepatic (by 39.1 and 41.8% in 30 and 100 mg/kg, respectively) and serum XO activity (by 30.7 and 50.1% in 30 and 100 mg/kg, respectively) in hyperuricemic mice. Moreover, several XO inhibitory and/or antihyperuricemic phytochemicals, such as stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, vitamin E, rutin, and kaempferol, were identified from CTLE. Compared with rutin, kaempferol showed markedly higher XO inhibitory activity in vitro. Our present results demonstrate that CTLE may offer a promising alternative to allopurinol for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the biologically active constituents of Camellia japonica leaf and anti-hyperuricemic effect in vitro and in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jun;39(6):1613-1620. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2973. Epub 2017 May 3. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28487949
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Quercus acuta Thunb. (Fagaceae) Extract: Active Constituents, Serum Uric Acid Suppression, and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:4097195. doi: 10.1155/2017/4097195. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28421120 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of extracts from Corylopsis coreana Uyeki (Hamamelidaceae) flos on xanthine oxidase activity and hyperuricemia.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;68(12):1597-1603. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12626. Epub 2016 Oct 2. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27696407
-
Quantitative Analysis, Extraction Optimization, and Biological Evaluation of Cudrania tricuspidata Leaf and Fruit Extracts.Molecules. 2017 Sep 7;22(9):1489. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091489. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28880226 Free PMC article.
-
From Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition to In Vivo Hypouricemic Effect: An Integrated Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies with Focus on Natural Molecules and Analogues.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 25;2020:9531725. doi: 10.1155/2020/9531725. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32184901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress as Mechanism of Reducing Hyperuricemia of Gardenia jasminoides-Poria cocos with Network Pharmacology.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 7;2021:8031319. doi: 10.1155/2021/8031319. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34917234 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential and pharmacological mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine in gout treatment.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May;46(5):1156-1176. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01459-6. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39825190 Review.
-
Strong inhibition of xanthine oxidase and elastase of Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC stem extract and analysis of biologically active constituents.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 25;14:1160330. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1160330. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37305531 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanolic Extract from Limonia acidissima L. Fruit Attenuates Serum Uric Acid Level via URAT1 in Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemic Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 9;16(3):419. doi: 10.3390/ph16030419. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986518 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Mechanism of Chinese Herbal Medicines in Lowering Serum Uric Acid Levels: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 25;11:578318. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.578318. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33568990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris M. D., Siegel L. B., Alloway J. A. Gout and hyperuricemia. American Family Physician. 1999;59(4):925–934. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

