Effects of exercise and physical activity promotion: meta-analysis informing the 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and hip/knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 30622734
- PMCID: PMC6307596
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000713
Effects of exercise and physical activity promotion: meta-analysis informing the 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and hip/knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of exercise and physical activity (PA) promotion on cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, flexibility, neuromotor performance (eg, balance) and daily PA in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA) and hip/knee osteoarthritis (HOA/KOA).
Methods: systematic review (SR) and meta-analysis (MA) were performed searching the databases PubMed/Medline, CENTRAL, Embase, Web of Science, Emcare and PsycInfo until April 2017. We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in adults (≥18 years) with RA, SpA and HOA/KOA, investigating the effects of exercise or PA promotion according to the public health PA recommendations by the American College of Sports Medicine. The time point of interest was the first assessment after the intervention period. If suitable, data were pooled in a MA using a random-effects model presented as standardised mean difference (SMD).
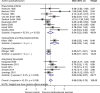
Results: The SR included 63 RCTs, of which 49 (3909 people with RA/SpA/HOA/KOA) were included in the MA. Moderate effects were found of aerobic exercises and resistance training on cardiovascular fitness (SMD 0.56 (95% CI 0.38 to 0.75)) and muscle strength (SMD 0.54 (95% CI 0.35 to 0.72)), respectively, but no effect of combined strength/aerobic/flexibility exercises on flexibility (SMD 0.12 (95% CI -0.16 to 0.41)). PA promotion interventions produced a small increase in PA behaviour (SMD 0.21 (95% CI 0.03 to 0.38)).
Conclusion: Exercises and PA promotion according to public health recommendations for PA improved cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength and PA behaviour, with moderate effect sizes in people with SpA, RA and HOA/KOA.
Trial registration number: CRD42017082131.
Keywords: knee osteoarthritis; osteoarthritis; rehabilitation; rheumatoid arthritis; spondyloarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, et al. . American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011;43:1334–59. 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb - DOI - PubMed
-
- Organization WH Global recommendations on physical activity for health. Geneve: Organization WH, 2010. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
