Maximum tolerated doses and erythropoiesis effects in the mouse bone marrow by 79 pesticides' technical materials assessed with the micronucleus assay
- PMID: 30622904
- PMCID: PMC6308258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.12.006
Maximum tolerated doses and erythropoiesis effects in the mouse bone marrow by 79 pesticides' technical materials assessed with the micronucleus assay
Abstract
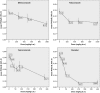
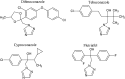
Effects of technical materials of pesticide active ingredients, belonging to various chemical classes, on erythropoiesis in mouse bone marrow were studied as part of the research on the pesticide mutagenic activity in micronucleus test. The purpose of the present study was to estimate the toxic action of the test substances on the target organ and the validity of the results of the micronucleus assay under conditions of erythropoiesis suppression. It was demonstrated that intragastrically administrated triazole pesticides reached bone marrow (target organ where micronucleus induction was assessed) and exerted an inhibitory effect on erythropoiesis. The effects of triazole pesticides were enhanced in the following order: difenoconazole ≤ tebuconazole < cyproconazole < flutriafol. Furthermore, an association between structural features of molecules and specific target organ activity of the test pesticides was observed. Based on the data on the general toxicity and the results of the evaluation of the effects on erythropoiesis, the maximum tolerated doses (MTDs) of 79 different technical materials of pesticides for CD-1 mice were determined.
Keywords: CI, confidence interval of the mean; Erythropoiesis; Es, total erythrocytes; MN test, micronucleus test; MTD, maximum tolerated dose; Maximum tolerated doses; Mice; Micronucleus test; NCE, normochromatic erythrocyte; PCE, polychromatic erythrocyte; Pesticides; Triazoles; mg/kg b.w., milligram per kilogram of body weight.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotoxicity of mixture of imidacloprid, imazalil and tebuconazole.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Aug 30;7:1090-1094. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.08.021. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32953461 Free PMC article.
-
The micronucleus test and erythropoiesis. Effects of erythropoietin and a mutagen on the ratio of polychromatic to normochromatic erythrocytes (P/N ratio).Mutagenesis. 1989 Nov;4(6):420-4. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.6.420. Mutagenesis. 1989. PMID: 2516221
-
Erythropoiesis and the induction of micronuclei in mouse spleen determined by flow cytometry.Mutat Res. 1997 Nov 27;394(1-3):17-28. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5718(97)00119-8. Mutat Res. 1997. PMID: 9434839
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010 Sep;(560):1, 7-31,33-171 passim. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010. PMID: 21037592 Review.
-
Bone marrow micronucleus assay: a review of the mouse stocks used and their published mean spontaneous micronucleus frequencies.Environ Mol Mutagen. 1994;23(4):239-73. doi: 10.1002/em.2850230402. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1994. PMID: 8013472 Review.
Cited by
-
The EU endocrine disruptors' regulation and the glyphosate controversy.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Jun 3;8:1193-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.05.013. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34150528 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Anti-Cytotoxic and Anti-Genotoxic Effects of Nigella sativa through a Micronucleus Test in BALB/c Mice.Nutrients. 2020 May 6;12(5):1317. doi: 10.3390/nu12051317. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32384595 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effects of the Sesquiterpenoid Valerenic Acid on Oxidative Stress Induced in HepG2 Cells after Exposure to the Fungicide Benomyl.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 8;10(5):746. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050746. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066673 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of acute toxicity and biochemical responses to chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin and their combination exposed earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Mar 30;6:288-297. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.03.007. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30989054 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity and mutagenicity assessment of a standardized extract (P2Et) obtained from Caesalpinia spinosa.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Dec 26;8:258-263. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.12.024. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33552924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OECDTestNo. 474: Mammalian Erythrocyte MicronucleusTest (2016).
-
- Fleming L.E., Timmeny W. Aplastic anemia and pesticides. An etiologic association? J. Occup. Med. 1993;35(11):1106–1116. - PubMed
-
- Prihartono N., Kriebel D., Woskie S., Thetkhathuek A., Sripaung N., Padungtod C., Kaufman D. Risk of aplastic anemia and pesticide and other chemical exposures. Asia Pac. J. Public Health. 2011;23(May (3)):369–377. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S., Basak P., Chaklader M., Das P., Pereira J.A., Chaudhuri S. Law S.PEsticide induced marrow toxicity and effects on marrow cell population and on hematopoietic stroma. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013;65(3):287–295. - PubMed
-
- Vardavas A.I., Fragkiadaki P., Alegakis A.K., Kouretas D., Goutzourelas N., Tsiaoussis J., Tsitsimpikou C., Stivaktakis P.D., Carvalho F., Tsatsakis A.M. Downgrading the systemic condition of rabbits after long term exposure to cypermethrin and piperonyl butoxide. Life Sci. 2016;145:114–120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

