Rare complications of multikinase inhibitor treatment
- PMID: 30624504
- PMCID: PMC10118667
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000090
Rare complications of multikinase inhibitor treatment
Abstract
Objective: The advent of multikinase inhibitor (MKI) therapy has led to a radical change in the treatment of patients with advanced thyroid carcinoma. The aim of this manuscript is to communicate rare adverse events that occurred in less than 5% of patients in clinical trials in a subset of patients treated in our hospital.
Subjects and methods: Out of 760 patients with thyroid cancer followed up with in our Division of Endocrinology, 29 (3.8%) received treatment with MKIs. The median age at diagnosis of these patients was 53 years (range 20-70), and 75.9% of them were women. Sorafenib was prescribed as first-line treatment to 23 patients with differentiated thyroid cancer and as second-line treatment to one patient with advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). Vandetanib was indicated as first-line treatment in 6 patients with MTC and lenvatinib as second-line treatment in two patients with progressive disease under sorafenib treatment.
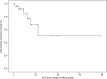
Results: During the follow-up of treatment (mean 13.7 ± 7 months, median 12 months, range 6-32), 5/29 (17.2%) patients presented rare adverse events. These rare adverse effects were: heart failure, thrombocytopenia, and squamous cell carcinoma during sorafenib therapy and squamous cell carcinoma and oophoritis with intestinal perforation during vandetanib treatment.
Conclusions: About 3 to 5 years after the approval of MKI therapy, we learned that MKIs usually lead to adverse effects in the majority of patients. Although most of them are manageable, we still need to be aware of potentially serious and rare or unreported adverse effects that can be life-threatening.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vandetanib for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic hereditary medullary thyroid cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Feb 10;28(5):767-72. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.6604. Epub 2010 Jan 11. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20065189 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sorafenib for the Treatment of Progressive Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Efficacy and Safety Analysis.Thyroid. 2016 Mar;26(3):414-9. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0334. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Thyroid. 2016. PMID: 26701095
-
Sorafenib in Japanese Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma.Thyroid. 2017 Sep;27(9):1142-1148. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0621. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Thyroid. 2017. PMID: 28635560 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Endocr J. 2020 Dec 28;67(12):1215-1226. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0171. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 32814730
-
Lenvatinib: Role in thyroid cancer and other solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Jan;42:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 26678514 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic Therapeutic Options in Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Current Indications and Optimal Timing.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 28;17(11):1800. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111800. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2019 European Thyroid Association Guidelines for the Treatment and Follow-Up of Advanced Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Cancer.Eur Thyroid J. 2019 Oct;8(5):227-245. doi: 10.1159/000502229. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Eur Thyroid J. 2019. PMID: 31768334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(7):621-30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical