Adolescent providers' knowledge of human papillomavirus vaccination age guidelines in five countries
- PMID: 30625017
- PMCID: PMC6746518
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1558688
Adolescent providers' knowledge of human papillomavirus vaccination age guidelines in five countries
Abstract
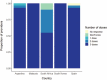
Purpose: To examine provider knowledge of HPV vaccination age guidelines in five countries. Methods: A total of 151 providers of adolescent vaccinations in Argentina, Malaysia, South Africa, South Korea, and Spain were interviewed between October 2013 and April 2014. Univariate analyses compared providers' understanding of recommended age groups for HPV vaccination to that of each country's national guidelines. Results: In three of five countries surveyed, most providers (97% South Africa, 95% Argentina, 87% Malaysia) included all nationally recommended ages in their target age group. However, a relatively large proportion of vaccinators in some countries (83% Malaysia, 55% Argentina) believed that HPV vaccination was recommended for women above age 26, far exceeding national guidelines, and beyond the maximum recommended age in the United States. National median minimum and maximum age recommendations cited by the respondents for HPV vaccination were 11 and 29 years in Argentina (national guideline: 11-14), 13 and 48 years in Malaysia (guideline 13-14), 8 and 14 years in South Africa (guideline 9-14), 10 and 20 years in South Korea (guideline 11-14), and 11 and 12 years in Spain (guideline 11-14). In all countries, a higher percentage of vaccinators included all nationally recommended ages for vaccination, as compared to providers who did not administer HPV vaccination. Conclusions: Overall, a substantial proportion of providers incorrectly reported their country's age guidelines for HPV vaccination, particularly the upper age limit. As provider recommendation is among the strongest predictors of successful vaccination uptake among adolescents, improved education and clarification of national guidelines for providers administering HPV vaccination is essential to optimize prevention of infection and associated disease.
Keywords: HPV; Human papillomavirus; adolescent; age guidelines; provider knowledge; vaccination.
Figures

References
-
- 2006 approval letter - human papillomavirus quadrivalent (types 6, 11, 16, 18) vaccine, recombinant. Rockville (MD): Department of Health and Human Services; 2006.
-
- Hartwig S, St Guily JL, Dominiak-Felden G, Alemany L, de Sanjosé S. Estimation of the overall burden of cancers, precancerous lesions, and genital warts attributable to 9-valent HPV vaccine types in women and men in Europe. Infect Agent Cancer. 2017;12(1):19. doi:10.1186/s13027-017-0129-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
