Evaluation of strategies for the assembly of diverse bacterial genomes using MinION long-read sequencing
- PMID: 30626323
- PMCID: PMC6325685
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5381-7
Evaluation of strategies for the assembly of diverse bacterial genomes using MinION long-read sequencing
Abstract
Background: Short-read sequencing technologies have made microbial genome sequencing cheap and accessible. However, closing genomes is often costly and assembling short reads from genomes that are repetitive and/or have extreme %GC content remains challenging. Long-read, single-molecule sequencing technologies such as the Oxford Nanopore MinION have the potential to overcome these difficulties, although the best approach for harnessing their potential remains poorly evaluated.
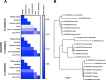
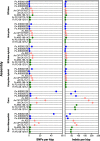
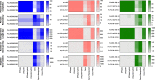
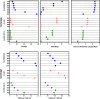
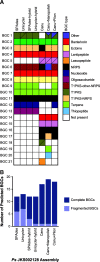
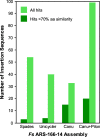
Results: We sequenced nine bacterial genomes spanning a wide range of GC contents using Illumina MiSeq and Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing technologies to determine the advantages of each approach, both individually and combined. Assemblies using only MiSeq reads were highly accurate but lacked contiguity, a deficiency that was partially overcome by adding MinION reads to these assemblies. Even more contiguous genome assemblies were generated by using MinION reads for initial assembly, but these assemblies were more error-prone and required further polishing. This was especially pronounced when Illumina libraries were biased, as was the case for our strains with both high and low GC content. Increased genome contiguity dramatically improved the annotation of insertion sequences and secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters, likely because long-reads can disambiguate these highly repetitive but biologically important genomic regions.
Conclusions: Genome assembly using short-reads is challenged by repetitive sequences and extreme GC contents. Our results indicate that these difficulties can be largely overcome by using single-molecule, long-read sequencing technologies such as the Oxford Nanopore MinION. Using MinION reads for assembly followed by polishing with Illumina reads generated the most contiguous genomes with sufficient accuracy to enable the accurate annotation of important but difficult to sequence genomic features such as insertion sequences and secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. The combination of Oxford Nanopore and Illumina sequencing can therefore cost-effectively advance studies of microbial evolution and genome-driven drug discovery.
Keywords: Genome assembly; Genome sequencing; Insertion sequences; Oxford Nanopore MinION; Secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
N/A
Consent for publication
N/A
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

