Cardiac profile of the Czech population of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients: a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study with T1 mapping
- PMID: 30626423
- PMCID: PMC6327529
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0986-0
Cardiac profile of the Czech population of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients: a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study with T1 mapping
Abstract
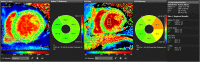
Background: The progressive cardiomyopathy that develops in boys with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy (DMD/BMD) is presumed to be a secondary consequence of the fibrosis within the myocardium. There are only limited data on using parametric imaging in these patients. The purpose of this study was to assess native T1 and extracellular volume (ECV) values in DMD patients.
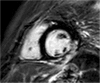
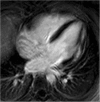
Methods: The Czech population of males with DMD/BMD was screened. All eligible patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were included. Forty nine males underwent cardiac magnetic resonance (MR) examination including T1 native and post-contrast mapping measurements. One DMD patient and all BMD patients were excluded from statistical analysis. Three groups were compared - Group D1 - DMD patients without late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) (n = 23), Group D2 - DMD patients with LGE (n = 20), and Group C - gender matched controls (n = 13).
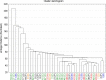
Results: Compared to controls, both DMD groups had prolonged T1 native relaxation time. These results are concordant in all 6 segments as well as in global values (1041 ± 31 ms and 1043 ± 37 ms vs. 983 ± 15 ms, both p < 0.05). Group D2 had significantly increased global ECV (0.28 ± 0.044 vs. 0.243 ± 0.013, p < 0.05) and segmental ECV in inferolateral and anterolateral segments in comparison with controls. The results were also significant after adjustment for subjects' age.
Conclusion: DMD males had increased native T1 relaxation time independent of the presence or absence of myocardial fibrosis. Cardiac MR may provide clinically useful information even without contrast media administration.
Keywords: Cardiac magnetic resonance; Cardiomyopathy; Duchene muscular dystrophy; T1 mapping; extracellular volume.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2000) of the World Medical Association, and was approved by the institutional ethics committee (University Hospital Brno, reference number 20130410–03). Written informed consent was obtained from the subjects and/or their legally authorized representative.
Consent for publication
No person’s personal data are published.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Van Deutekom JC, Fokkema IF, Van Ommen GJ, Den Dunnen JT. Entries in the Leiden Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutation database: an overview of mutation types and paradoxical cases that confirm the reading-frame rule. Muscle Nerve. 2006;34(2):135–144. doi: 10.1002/mus.20586. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

