TMPRSS2 Contributes to Virus Spread and Immunopathology in the Airways of Murine Models after Coronavirus Infection
- PMID: 30626688
- PMCID: PMC6401451
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01815-18
TMPRSS2 Contributes to Virus Spread and Immunopathology in the Airways of Murine Models after Coronavirus Infection
Abstract
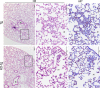
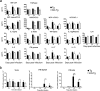
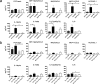
Transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 activates the spike protein of highly pathogenic human coronaviruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV). In vitro, activation induces virus-cell membrane fusion at the cell surface. However, the roles of TMPRSS2 during coronavirus infection in vivo are unclear. Here, we used animal models of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infection to investigate the role of TMPRSS2. Th1-prone C57BL/6 mice and TMPRSS2-knockout (KO) mice were used for SARS-CoV infection, and transgenic mice expressing the human MERS-CoV receptor DPP4 (hDPP4-Tg mice) and TMPRSS2-KO hDPP4-Tg mice were used for MERS-CoV infection. After experimental infection, TMPRSS2-deficient mouse strains showed reduced body weight loss and viral kinetics in the lungs. Lack of TMPRSS2 affected the primary sites of infection and virus spread within the airway, accompanied by less severe immunopathology. However, TMPRSS2-KO mice showed weakened inflammatory chemokine and/or cytokine responses to intranasal stimulation with poly(I·C), a Toll-like receptor 3 agonist. In conclusion, TMPRSS2 plays a crucial role in viral spread within the airway of murine models infected by SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV and in the resulting immunopathology.IMPORTANCE Broad-spectrum antiviral drugs against highly pathogenic coronaviruses and other emerging viruses are desirable to enable a rapid response to pandemic threats. Transmembrane protease serine type 2 (TMPRSS2), a protease belonging to the type II transmembrane serine protease family, cleaves the coronavirus spike protein, making it a potential therapeutic target for coronavirus infections. Here, we examined the role of TMPRSS2 using animal models of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infection. The results suggest that lack of TMPRSS2 in the airways reduces the severity of lung pathology after infection by SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Taken together, the results will facilitate development of novel targets for coronavirus therapy.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; SARS-CoV; TMPRSS2; animal model; immunopathology.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

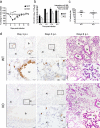
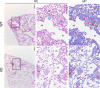
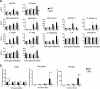
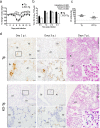
References
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, Tong S, Urbani C, Comer JA, Lim W, Rollin PE, Dowell SF, Ling AE, Humphrey CD, Shieh WJ, Guarner J, Paddock CD, Rota P, Fields B, DeRisi J, Yang JY, Cox N, Hughes JM, LeDuc JW, Bellini WJ, Anderson LJ, SARS Working Group. 2003. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 348:1953–1966. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030781. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Rabenau H, Panning M, Kolesnikova L, Fouchier RA, Berger A, Burguiere AM, Cinatl J, Eickmann M, Escriou N, Grywna K, Kramme S, Manuguerra JC, Muller S, Rickerts V, Sturmer M, Vieth S, Klenk HD, Osterhaus AD, Schmitz H, Doerr HW. 2003. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 348:1967–1976. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030747. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peiris JSM, Lai ST, Poon LLM, Guan Y, Yam LYC, Lim W, Nicholls J, Yee WKS, Yan WW, Cheung MT, Cheng VCC, Chan KH, Tsang DNC, Yung RWH, Ng TK, Yuen KY. 2003. Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet 361:1319–1325. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13077-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhong NS, Zheng BJ, Li YM, Poon LLM, Xie ZH, Chan KH, Li PH, Tan SY, Chang Q, Xie JP, Liu XQ, Xu J, Li DX, Yuen KY, Peiris JSM, Guan Y. 2003. Epidemiology and cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong, People's Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet 362:1353–1358. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14630-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

