Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
- PMID: 30627240
- PMCID: PMC6323585
- DOI: 10.5114/pjr.2018.76380
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: two steroid-responsive cases
Abstract
Purpose: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is characterised by orthostatic headache, low cerebrospinal fluid pressure and diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement after intravenous gadolinium contrast administration. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) often plays a crucial role for correct diagnosis.
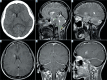
Case description: We described two similar cases of SIH, whose clinical and imaging features are typical for this pathology. At MRI brain scan, both patients showed diffuse and intense pachymeningeal enhancement and moderate venous distension and epidural vein engorgement. The two patients were treated with bed rest and oral steroid therapy, with complete and long-lasting symptomatic relief.
Conclusions: Orthostatic nature of headache is the most indicative clinical feature suggesting SIH; contrast-enhanced MRI provides definite imaging diagnostic findings. Conservative treatment coupled to steroid therapy is often sufficient to obtain complete disappearance of symptoms.
Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure; myelopathy; spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH).
Figures



References
-
- Paldino M, Mogilner AY, Tenner MS. Intracranial hypotension syndrome: a comprehensive review. Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15:ECP2. - PubMed
-
- Schievink WI, Dodick DW, Mokri B, et al. diagnostic criteria for headache due to spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a perspective. Headache. 2011;51:1442–1444. - PubMed
-
- Mokri B. Spontaneous CSF leaks: low CSF volume syndromes. Neurol Clin. 2014;32:397–422. - PubMed
-
- Savoiardo M, Minati L, Farina L, et al. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension with deep brain swelling. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 7):1884–1893. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
