Descriptive analysis of colorectal cancer in Zambia, Southern Africa using the National Cancer Disease Hospital Database
- PMID: 30627309
- PMCID: PMC6307926
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2018.30.248.12464
Descriptive analysis of colorectal cancer in Zambia, Southern Africa using the National Cancer Disease Hospital Database
Abstract
Introduction: Colon cancer is preventable. There is a plethora of data regarding epidemiology and screening guidelines, however this data is sparse from the African continent. Objective: we aim to evaluate the trends of colorectal cancer (CRC) in a native African population based on age at diagnosis, gender and stage at diagnosis.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of the Cancer Disease Hospital (CDH) registry in Zambia, Southern Africa.
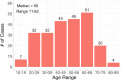
Results: 377 charts were identified in the CDH registry between 2007 and 2015, of which 234 were included in the final analysis. The mean age at diagnosis was 48.6 years and 62% are males. Using descriptive analysis for patterns: mode of diagnosis was surgical in 195 subjects (84%), histology adenocarcinoma in 225 (96.5%), most common location is rectum 124 (53%) followed by sigmoid 31 (13.4%), and cecum 26 (11%). 122 subjects (54%) were stage 4 at diagnosis. Using the Spearman rank correlation, we see no association between year and stage at diagnosis (p = 0.30) or year and age at diagnosis (p = 0.92).
Conclusion: Colorectal cancer was diagnosed at a young age and late stage in the Zambian patients.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; cancer in Africa; colon cancer; non-communicable diseases; rectal cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Jemal A, Ward EM. Increase in incidence of colorectal cancer among young men and women in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(6):1695–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical