A Case of Recurrent Esophageal Cancer Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy in Pregnancy
- PMID: 30627462
- PMCID: PMC6304601
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1280582
A Case of Recurrent Esophageal Cancer Treated with Concurrent Chemoradiation Therapy in Pregnancy
Abstract
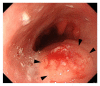
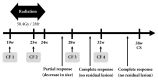
Esophageal cancer rarely coincides with pregnancy, and only five cases have been reported thus far. The management of esophageal cancer during pregnancy is extremely challenging due to its aggressive nature. We herein report a case of recurrent esophageal cancer in pregnancy. A 41-year-old multigravida with a history of esophageal squamous cell cancer treated with esophagectomy and perioperative chemotherapy was diagnosed with local recurrent carcinoma of the residual esophagus at 16 weeks of gestation. The patient strongly desired to continue the pregnancy, and concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CRT) consisting of 50.4 Gy of radiation, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil was carried out from 19 weeks of gestation. CRT was dramatically effective, and the recurrent lesion disappeared. At 38 weeks of gestation, she underwent cesarean section and delivered a healthy female baby. Both maternal and fetal courses were satisfactory, and the patient has been free of disease for 12 months. This is the first case of recurrent esophageal cancer in pregnancy in which CRT was completed without reducing treatment intensity and led to a complete response. Nevertheless, little is known regarding the safety and possible adverse effects of CRT on the fetus. Therefore, deliberate selection of patients and long-term follow-up of the child are necessary.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Management of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with chemoradiation alone or chemoradiation followed by esophagectomy: results of sequential nonrandomized phase II studies.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995 Jun 15;32(3):753-61. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)00592-9. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995. PMID: 7790262 Clinical Trial.
-
Final Results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0246: An Organ-Preserving Selective Resection Strategy in Esophageal Cancer Patients Treated with Definitive Chemoradiation.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Feb;12(2):368-374. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 8. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27729298 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[A Case of Local Recurrence of Esophageal Cancer after Chemoradiation Therapy Successfully Treated with Nivolumab].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2023 Dec;50(13):1444-1446. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2023. PMID: 38303302 Japanese.
-
[Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and concurrent radiochemotherapy for advanced esophageal carcinoma potentially invading adjacent structures].Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997 Sep;98(9):761-6. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9370136 Review. Japanese.
-
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy before transhiatal esophagectomy for esophageal carcinoma.Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 Mar;49(3):348-54; discussion 354-5. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90237-z. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990. PMID: 2106845 Review.
Cited by
-
A case report of metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma during pregnancy.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2024 Aug 16;12:2050313X241266758. doi: 10.1177/2050313X241266758. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39161919 Free PMC article.
-
Transhiatal esophagectomy for distal esophageal cancer during pregnancy: A rare and challenging case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Jul;120:109902. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.109902. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38878733 Free PMC article.
-
A case of a pregnant woman with locally advanced cervical esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy.Int Cancer Conf J. 2022 Jul 4;11(4):292-297. doi: 10.1007/s13691-022-00564-9. eCollection 2022 Oct. Int Cancer Conf J. 2022. PMID: 36186226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pavlidis N. A. Coexistence of pregnancy and malignancy. The Oncologist. 2002;7(4):279–287. - PubMed
-
- Minsky B. D., Pajak T. F., Ginsberg R. J., et al. INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94-05) phase III trial of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: high-dose versus standard-dose radiation therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2002;20(5):1167–1174. doi: 10.1200/jco.20.5.1167. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

