Application of high-performance magnetic nanobeads to biological sensing devices
- PMID: 30627798
- PMCID: PMC6453870
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1548-y
Application of high-performance magnetic nanobeads to biological sensing devices
Abstract
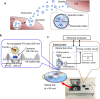
Nanomaterials have extensive applications in the life sciences and in clinical diagnosis. We have developed magnetic nanoparticles with high dispersibility and extremely low nonspecific binding to biomolecules and have demonstrated their application in chemical biology (e.g., for the screening of drug receptor proteins). Recently, the excellent properties of nanobeads have made possible the development of novel rapid immunoassay systems and high-precision technologies for exosome detection. For immunoassays, we developed a technology to encapsulate a fluorescent substance in magnetic nanobeads. The fluorescent nanobeads allow the rapid detection of a specific antigen in solution or in tissue specimens. Exosomes, which are released into the blood, are expected to become markers for several diseases, including cancer, but techniques for measuring the absolute quantity of exosomes in biological fluids are lacking. By integrating magnetic nanobead technology with an optical disc system, we developed a novel method for precisely quantifying exosomes in human serum with high sensitivity and high linearity without requiring enrichment procedures. This review focuses on the properties of our magnetic nanobeads, the development of novel biosensors using these nanobeads, and their broad practical applications. Graphical abstract ᅟ.
Keywords: Biosensor; Exosome; Immunoassay; Liquid biopsy; Magnetic nanobeads.
Conflict of interest statement
M.H. is a full-time employee of Tamagawa Seiki Co. Ltd. M.I. is a full-time employee of JVCKENWOOD Corporation. H.H. is a technical advisor at JVCKENWOOD Corporation. The authors have no other competing financial and nonfinancial interests regarding the content of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Weaver JC, Vaughan TE, Astumian RD. Biological sensing of small field differences by magnetically sensitive chemical reactions. Nature. 2000;405(6787):707–709. - PubMed
-
- Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255–289. - PubMed
-
- Llandro J, Palfreyman JJ, Ionescu A, Barnes CH. Magnetic biosensor technologies for medical applications: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010;48(10):977–998. - PubMed
-
- Fratila RM, Moros M, de la Fuente JM. Recent advances in biosensing using magnetic glyconanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(7):1783–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

