Biomarkers enhance the long-term predictive ability of the KAMIR risk score in Chinese patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 30628957
- PMCID: PMC6629309
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000015
Biomarkers enhance the long-term predictive ability of the KAMIR risk score in Chinese patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) score is recommended by current ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) guidelines. But it has inherent defects. The present study aimed to investigate the more compatible risk stratification for Chinese patients with STEMI and to determine whether the addition of biomarkers to the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry (KAMIR) score could enhance its predictive value for long-term outcomes.
Methods: A total of 1093 consecutive STEMI patients were included and followed up 48.2 months. Homocysteine, hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were detected. The KAMIR score and the GRACE score were calculated. The performance between the KAMIR and the GRACE was compared. The predictive power of the KAMIR alone and combined with biomarkers were assessed by the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
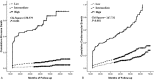
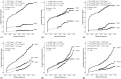
Results: The KAMIR demonstrated a better risk stratification and predictive ability than the GRACE (death: AUC = 0.802 vs. 0.721, P < 0.001; major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE): AUC = 0.683 vs. 0.656, P < 0.001). It showed that the biomarkers could independently predict death [homocysteine: HR = 1.019 (1.015-1.024), P < 0.001; hs-CRP: HR = 1.052 (1.000-1.104), P = 0.018; NT-pro BNP: HR = 1.142 (1.004-1.280), P = 0.021] and MACE [homocysteine: HR = 1.019 (1.015-1.024), P < 0.001; hs-CRP: HR = 1.012 (1.003-1.021), P = 0.020; NT-pro BNP: HR = 1.136 (1.104-1.168), P = 0.006]. When they were used in combination with the KAMIR, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) significantly increased for death [homocysteine: AUC = 0.802 vs. 0.890, Z = 5.982, P < 0.001; hs-CRP: AUC = 0.802 vs. 0.873, Z = 3.721, P < 0.001; NT-pro BNP: AUC = 0.802 vs. 0.871, Z = 2.187, P = 0.047; homocysteine, hs-CRP and NT-pro BNP: AUC = 0.802 vs. 0.940, Z = 6.177, P < 0.001] and MACE [homocysteine: AUC = 0.683 vs. 0.771, Z = 6.818, P < 0.001; hs-CRP: AUC = 0.683 vs. 0.712, Z = 2.022, P = 0.031; NT-pro BNP: AUC = 0.683 vs. 0.720, Z = 2.974, P = 0.003; homocysteine, hs-CRP and NT-pro BNP: AUC = 0.683 vs. 0.789, Z = 6.900, P < 0.001].
Conclusion: The KAMIR is better than the GRACE in risk stratification and prognosis prediction in Chinese STEMI patients. A combination of above-mentioned biomarkers can develop a more predominant prediction for long-term outcomes.
Figures


References
-
- Qiu JP, Zhang Q, Lu JD, Wang HR, Lin J, Ge ZR, et al. Direct ambulance transport to catheterization laboratory reduces door-to-balloon time in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: the DIRECT-STEMI study. Chin Med J 2011; 124:805–810. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2011.06.002. - PubMed
-
- O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Tommaso CL. American College of Emergency P, Society for Cardiovascular A, Interventions 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 61:e78–e140. doi: 10.1002/ccd.24776. - PubMed
-
- Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, Badano LP, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Borger MA, et al. Task Force on the management of ST seamiot ESoC ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 2012; 33:2569–2619. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs215. - PubMed
-
- Zhao FH, Chen YD, Song XT, Pan WQ, Jin ZN, Yuan F, et al. Predictive factors of recurrent angina after acute coronary syndrome: the global registry acute coronary events from China (Sino-GRACE). Chin Med J 2008; 121:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Yan AT, Yan RT, Tan M, Casanova A, Labinaz M, Sridhar K, et al. Risk scores for risk stratification in acute coronary syndromes: useful but simpler is not necessarily better. Eur Heart J 2007; 28:1072–1078. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

