Norepinephrine regulation of ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus metabolic transmitter biomarker and astrocyte enzyme and receptor expression: Impact of 5' AMP-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 30629946
- PMCID: PMC6430699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.01.012
Norepinephrine regulation of ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus metabolic transmitter biomarker and astrocyte enzyme and receptor expression: Impact of 5' AMP-activated protein kinase
Abstract
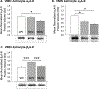
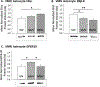
The ventromedial hypothalamic energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) maintains glucostasis via neurotransmitter signals that diminish [γ-aminobutyric acid] or enhance [nitric oxide] counter-regulation. Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus (VMN) 'fuel-inhibited' neurons are sensitive to astrocyte-generated metabolic substrate stream. Norepinephrine (NE) regulates astrocyte glycogen metabolism in vitro, and hypoglycemia intensifies VMN NE activity in vivo. Current research investigated the premise that NE elicits AMPK-dependent adjustments in VMN astrocyte glycogen metabolic enzyme [glycogen synthase (GS); glycogen phosphorylase (GP)] and gluco-regulatory neuron biomarker [glutamate decarboxylase65/67 (GAD); neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS); SF-1] protein expression in male rats. We also examined whether VMN astrocytes are directly receptive to NE and if noradrenergic input regulates cellular sensitivity to the neuro-protective steroid estradiol. Intra-VMN NE correspondingly augmented or reduced VMN tissue GAD and nNOS protein despite no change in circulating glucose, data that imply that short-term exposure to NE promotes persistent improvement in VMN nerve cell energy stability. The AMPK inhibitor Compound C (Cc) normalized VMN nNOS, GS, and GP expression in NE-treated animals. NE caused AMPK-independent down-regulation of alpha2-, alongside Cc-reversible augmentation of beta1-adrenergic receptor protein profiles in laser-microdissected astrocytes. NE elicited divergent adjustments in astrocyte estrogen receptor-beta (AMPK-unrelated reduction) and GPR-30 (Cc-revocable increase) proteins. Outcomes implicate AMPK in noradrenergic diminution of VMN nitrergic metabolic-deficit signaling and astrocyte glycogen shunt activity. Differentiating NE effects on VMN astrocyte adrenergic and estrogen receptor variant expression suggest that noradrenergic regulation of glycogen metabolism may be mediated, in part, by one or more receptors characterized here by sensitivity to this catecholamine.
Keywords: Compound C; GPR-30; Glycogen synthase; Neuronal nitric oxide synthase; Norepinephrine; Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Alhamami HN, Alshamrani A, Briski KP. Effects of the glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor 1,4-dideoxy1,4-imino-D-arabinitol on ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity and metabolic neurotransmitter biosynthetic enzyme protein expression in eu- versus hypoglycemic male rats. Physiol. Reports 2018; 103: 236–249.
-
- Ashford MLJ, Boden PR, Treherne JM. Glucose-induced excitation of hypothalamic neurons is mediated by ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pfugers Arch. 415: 479–483, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Arevalo MA, Santos-Galindo M, Bellini MJ, Azcoitia I, Garcia-Segura LM. Actions of estrogens on glial cells: Implications for neuroprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010; 1800: 1106–1112. - PubMed
-
- Azcoitia I, Sierra A, Garcia-Segura LM. Localization of estrogen receptor beta-immunoreactivity in astrocytes of the adult rat brain. Glia 1999; 26: 260–267. - PubMed
-
- Barros LF. Metabolic signaling by lactate in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 36: 396–404, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

