Estimating the clinical cost of drug development for orphan versus non-orphan drugs
- PMID: 30630499
- PMCID: PMC6327525
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0990-4
Estimating the clinical cost of drug development for orphan versus non-orphan drugs
Abstract
Background: High orphan drug prices have gained the attention of payers and policy makers. These prices may reflect the need to recoup the cost of drug development from a small patient pool. However, estimates of the cost of orphan drug development are sparse.
Methods: Using publicly available data, we estimated the differences in trial characteristics and clinical development costs with 100 orphan and 100 non-orphan drugs.
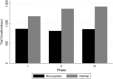
Results: We found that the out-of-pocket clinical costs per approved orphan drug to be $166 million and $291 million (2013 USD) per non-orphan drug. The capitalized clinical costs per approved orphan drug and non-orphan drug were estimated to be $291 million and $412 million respectively. When focusing on new molecular entities only, we found that the capitalized clinical cost per approved orphan drug was half that of a non-orphan drug.
Conclusions: More discussion is needed to better align on which cost components should be included in research and development costs for pharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Cost of drug development; Orphan drugs; Rare diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not Applicable
Consent for publication
Not Applicable
Competing interests
KJ is currently a full time employee at Hoffmann-la Roche. MM reports receiving honoraria for serving on Advisory Boards for Astra Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Glaxo Smith Kline, Hoffmann-la Roche, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. PG, MK, AH and JSH have no conflicts of interest to report.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Field MJ, B.T., editors, Rare Diseases and Orphan Products: Accelerating Research and Development. 2010, Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). - PubMed
-
- EvaluatePharma . Orphan Drug Report 2017. 2017.

