CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies
- PMID: 30630983
- PMCID: PMC6355473
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2018.197152
CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies
Abstract
Primary cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders are the second most common subgroup of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. They include two clinically different entities with some overlapping features and borderline cases: lymphomatoid papulosis and primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Molecular studies of primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma reveal an increasing level of heterogeneity that is associated with histological and immunophenotypic features of the cases and their response to specific therapies. Here, we review the most significant genetic, epigenetic and molecular alterations described to date in primary cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, and their potential as therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2019 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
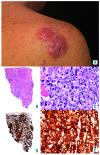
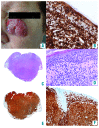
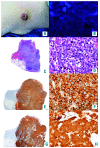
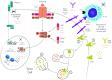
References
-
- Macaulay WL. Lymphomatoid papulosis. A continuing self-healing eruption, clinically benign–histologically malignant. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97(1):23–30. - PubMed
-
- Nijsten T, Curiel-Lewandrowski C, Kadin ME. Lymphomatoid papulosis in children: a retrospective cohort study of 35 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140(3):306–312. - PubMed
-
- Kempf W. A new era for cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2017;34(1):22–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

