Self-Generation in the Context of Inquiry-Based Learning
- PMID: 30631290
- PMCID: PMC6315139
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02440
Self-Generation in the Context of Inquiry-Based Learning
Abstract
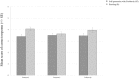
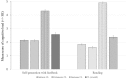
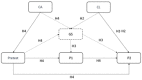
Self-generation of knowledge can activate deeper cognitive processing and improve long-term retention compared to the passive reception of information. It plays a distinctive role within the concept of inquiry-based learning, which is an activity-oriented, student-centered collaborative learning approach in which students become actively involved in knowledge construction by following an idealized hypothetico-deductive method. This approach allows students to not only acquire content knowledge, but also an understanding of investigative procedures/inquiry skills - in particular the control-of-variables strategy (CVS). From the perspective of cognitive load theory, generating answers and solutions during inquiry-based learning is inefficient as it imposes an intrinsic and extraneous load on learners. Previous research on self-generation of content knowledge in inquiry-based learning has demonstrated that (1) a high cognitive load impairs retention of the generated information, (2) feedback is a fundamental requirement for self-generation of complex content knowledge, (3) self-generation success is key to long-term retention, and (4) generating and rereading place different demands on learners. However, there is still no research on the self-generation of scientific reasoning skills (procedural knowledge) and no knowledge of interaction between the (long-term) retention of these skills with prior knowledge, feedback and self-generation success. That is why this experiment was conducted. The focus of this research is to analyze the distinctive role of self-generation of scientific reasoning skills within the concept of inquiry-based learning and to identify the influence of prior knowledge and self-generation success on short-term and long-term retention. For this purpose, an experiment involving 133 6th and 7th graders was conducted. An inquiry activity that included the self-generation of scientific reasoning skills was compared to an inquiry task that had students simply read information about the experimental design. We used both an immediate and a delayed test to examine which treatment better developed a deeper understanding of CVS and an ability to apply this knowledge to novel problems (transfer). Direct instruction was clearly superior to self-generation in facilitating students' acquisition of CVS immediately after the inquiry task. However, after a period of 1 week had elapsed, both treatment conditions turned out to be equally effective. A generation effect was only found among students with high self-generation success after a 1-week delay.
Keywords: control of variables strategy; generation effect; inquiry-based learning; prior knowledge; scientific reasoning skills; self-generation success.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold J. C., Kremer K., Mayer J. (2014). Understanding Students’ experiments-what kind of support do they need in inquiry tasks? Int. J. Sci. Educ. 36 2719–2749. 10.1080/09500693.2014.930209 - DOI
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Bjork E., Bjork R. (2011). “Making things hard on yourself, but in a good way: creating desirable difficulties to enhance learning,” in Psychology and the Real World: Essays Illustrating Fundamental Contributions to Society eds Gernsbacher M. A., Pew R. W., Hough L. M., Pomerantz J. R. (New York, NY: Worth Publishers; ) 56–64.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

