Tocilizumab Effectiveness After Switching from Intravenous to Subcutaneous Route in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: The RoSwitch Study
- PMID: 30632015
- PMCID: PMC6393270
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-018-0138-y
Tocilizumab Effectiveness After Switching from Intravenous to Subcutaneous Route in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: The RoSwitch Study
Abstract
Introduction: The main objective of this work was to assess the maintenance of effectiveness of subcutaneous tocilizumab 6 months after switching from intravenous to subcutaneous formulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a real-world setting. Secondary objectives aimed to describe the characteristics of patients and disease, the effectiveness at 12 months after switching, the therapeutic maintenance, and to search for predictive factors of switching.
Methods: We analyzed all the RA patients of the shared medical file "RIC Nord de France", treated with tocilizumab, switching or not from intravenous to subcutaneous tocilizumab, between April 2015 and January 2016. The primary effectiveness endpoint was the proportion of patients remaining in their DAS28-ESR category remission/low disease activity (LDA) or moving to an inferior DAS28-ESR category at 6 months. Since RoSwitch was an observational study, without randomization, a propensity score was built in a sensitivity analysis to balance on RA and patients' characteristics at inclusion between switching and no-switching groups.
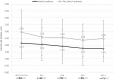
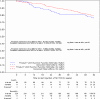
Results: An improvement of initial DAS28-ESR category or maintenance in DAS28-ESR remission/LDA at 6 months was shown in 203 of the 285 patients with an evaluation for the primary criterion (71.2%, 95% CI [65.6-76.4%]) without differences between groups (73.3%, 95% CI [63.0-82.1%] vs. 70.3%, 95% CI [63.3-76.6%]). The RoSwitch study showed the maintenance of effectiveness at 6 and 12 months. Similar therapeutic maintenance rates were observed for switch and no-switch patients. No clinical factor was associated with the switch in patients in remission/LDA at inclusion.
Conclusions: The RoSwitch study showed the maintenance of effectiveness at 6 months in RA patients switching from intravenous (IV) to subcutaneous (SC) tocilizumab.
Funding: Roche SAS and Chugai Pharma France.
Keywords: Administration route; Rheumatoid arthritis; Subcutaneous; Switch; Tocilizumab.
Figures

References
-
- Fautrel B, Gaujoux-Viala C. Aspects médico-économiques de la polyarthrite Rhumatoïde. Bull Acad Natle Méd. 2012;196(7):1295–1306. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, et al. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(11):1516–1523. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.092932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

