Influenza virus inoculum volume is critical to elucidate age-dependent mortality in mice
- PMID: 30632262
- PMCID: PMC6413738
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12893
Influenza virus inoculum volume is critical to elucidate age-dependent mortality in mice
Abstract
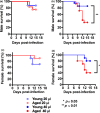
The elderly exhibit increased mortality to influenza viral infection for unclear reasons. Mice are frequently used to model how aging impacts disease. Several studies have shown that aged mice exhibit an increased mortality to influenza virus, but two recent studies demonstrated the opposite. These two studies administered the virus intranasally in 20 µL, whereas the other studies used a viral inoculum in at least 30 µL. To determine whether the volume of the inoculum could explain the conflicting reports, we infected young and aged mice via intranasal instillation of 40 µL or 20 µL containing 1 x 104 plaque-forming units (PFU) of H1N1 influenza virus. We found that intranasal administration of 40 µL but not 20 µL of inoculum resulted in age-dependent mortality in mice. Compared to aged mice infected with 40 µL inoculum, those infected with 20 µL inoculum showed reduced levels of live virus and IFN-β in the lung 3 days postinfection. Furthermore, aged mice administered 40 µL of Evans blue intranasally displayed increased dye retention in their bronchoalveolar lavage fluid compared to those administered 20 µL of Evans blue. Our data demonstrate that the inoculating volume of virus is critical for adequate delivery of influenza virus to the lung and thus for efficient infection of aged mice. These findings shed light on discrepant results in the literature regarding aged mice and influenza infection, and establish that mice can be used to examine how aging impacts the response to this biomedically important infection.
© 2019 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

