Preliminary experience with the multisensor HeartLogic algorithm for heart failure monitoring: a retrospective case series report
- PMID: 30632306
- PMCID: PMC6437441
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12394
Preliminary experience with the multisensor HeartLogic algorithm for heart failure monitoring: a retrospective case series report
Abstract
Aims: In the Multisensor Chronic Evaluation in Ambulatory Heart Failure Patients study, a novel algorithm for heart failure (HF) monitoring was implemented. The HeartLogic (Boston Scientific) index combines data from multiple implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)-based sensors and has proved to be a sensitive and timely predictor of impending HF decompensation. The remote monitoring of HF patients by means of HeartLogic has never been described in clinical practice. We report post-implantation data collected from sensors, the combined index, and their association with clinical events during follow-up in a group of patients who received a HeartLogic-enabled device in clinical practice.
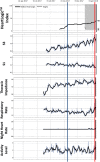
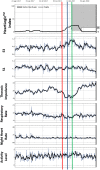
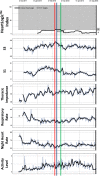
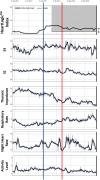
Methods and results: Patients with ICD and cardiac resynchronization therapy ICD were remotely monitored. In December 2017, the HeartLogic feature was activated on the remote monitoring platform, and multiple ICD-based sensor data collected since device implantation were made available: HeartLogic index, heart rate, heart sounds, thoracic impedance, respiration, and activity. Their association with clinical events was retrospectively analysed. Data from 58 patients were analysed. During a mean follow-up of 5 ± 3 months, the HeartLogic index crossed the threshold value (set by default to 16) 24 times (over 24 person-years, 0.99 alerts/patient-year) in 16 patients. HeartLogic alerts preceded five HF hospitalizations and five unplanned in-office visits for HF. Symptoms or signs of HF were also reported at the time of five scheduled visits. The median early warning time and the time spent in alert were longer in the case of hospitalizations than in the case of minor events of clinical deterioration of HF. HeartLogic contributing sensors detected changes in heart sound amplitude (increased third sound and decreased first sound) in all cases of alerts. Patients with HeartLogic alerts during the observation period had higher New York Heart Association class (P = 0.025) and lower ejection fraction (P = 0.016) at the time of activation.
Conclusions: Our retrospective analysis indicates that the HeartLogic algorithm might be useful to detect gradual worsening of HF and to stratify risk of HF decompensation.
Keywords: CRT; Decompensation; Heart failure; ICD; Telemedicine.
© 2019 The Authors ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Campari and S. Valsecchi are employees of Boston Scientific. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance of a multisensor implantable defibrillator algorithm for heart failure monitoring related to co-morbidities.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Aug;10(4):2469-2478. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14416. Epub 2023 Jun 5. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37278122 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective evaluation of the multisensor HeartLogic algorithm for heart failure monitoring.Clin Cardiol. 2020 Jul;43(7):691-697. doi: 10.1002/clc.23366. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Clin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32304098 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Algorithm for Heart Failure Risk Stratification and Management: An Analysis in Clinical Practice.Circ Heart Fail. 2021 Oct;14(10):e008134. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.008134. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Circ Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 34190592 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Multisensor CIED-based Heart Failure Monitoring on Mortality, Heart Failure Hospitalizations and Outpatient Visits: A Systematic Review.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2025 Jul 1;22(1):21. doi: 10.1007/s11897-025-00707-y. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2025. PMID: 40591072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Detection of Fluid Retention in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure: A Review of a Novel Multisensory Algorithm, HeartLogicTM.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;21(4):1361. doi: 10.3390/s21041361. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heart failure decompensation alerts in a patient's home using an automated, AI-driven, point-of-care device.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Apr 12;15(4):e248682. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-248682. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35414581 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal changes of cardiac acoustic biomarkers and cardiac function in acute decompensated heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Oct;8(5):4037-4047. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13492. Epub 2021 Jun 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 34184415 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of a multisensor implantable defibrillator algorithm for heart failure monitoring related to co-morbidities.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Aug;10(4):2469-2478. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14416. Epub 2023 Jun 5. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37278122 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Monitoring in Heart Failure: Revolutionizing Patient Management and Outcomes.US Cardiol. 2024 Dec 20;18:e23. doi: 10.15420/usc.2024.23. eCollection 2024. US Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39872827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Steep Increase in the HeartLogic Index Predicts COVID-19 Disease in an Advanced Heart Failure Patient.Case Rep Cardiol. 2020 Jul 11;2020:8896152. doi: 10.1155/2020/8896152. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32733711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, ESC Scientific Document Group . 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Conraads VM, Tavazzi L, Santini M, Oliva F, Gerritse B, Yu CM, Cowie MR. Sensitivity and positive predictive value of implantable intrathoracic impedance monitoring as a predictor of heart failure hospitalizations: the SENSE‐HF trial. Eur Heart J 2011; 32: 2266–2273. - PubMed
-
- van Veldhuisen DJ, Braunschweig F, Conraads V, Ford I, Cowie MR, Jondeau G, Kautzner J, Aguilera RM, Lunati M, Yu CM, Gerritse B, Borggrefe M, DOT‐HF Investigators . Intrathoracic impedance monitoring, audible patient alerts, and outcome in patients with heart failure. Circulation 2011; 124: 1719–1726. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Varma N, Kacet S, Lewalter T, Søgaard P, Guédon‐Moreau L, Proff J, Gerds TA, Anker SD, Torp‐Pedersen C. Daily remote monitoring of implantable cardioverter‐defibrillators: insights from the pooled patient‐level data from three randomized controlled trials (IN‐TIME, ECOST, TRUST). Eur Heart J 2017; 38: 1749–1755. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boriani G, Da Costa A, Quesada A, Ricci RP, Favale S, Boscolo G, Clementy N, Amori V, Mangoni Di S, Stefano L, Burri H, MORE‐CARE Study Investigators . Effects of remote monitoring on clinical outcomes and use of healthcare resources in heart failure patients with biventricular defibrillators: results of the MORE‐CARE multicentre randomized controlled trial. Eur J Heart Fail 2017; 19: 416–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

