Characterization of the Effect of Renal Impairment on Upadacitinib Pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 30633369
- PMCID: PMC6590375
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.1375
Characterization of the Effect of Renal Impairment on Upadacitinib Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
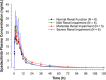
Upadacitinib is a novel selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor developed for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. The objective of this study was to assess the pharmacokinetics and safety of a single upadacitinib dose in subjects with normal renal function and in subjects with renal impairment. A total of 24 subjects between the ages of 18 and 75 years were assigned to 1 of 4 renal function groups based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (normal, mild, moderate, severe; N = 6/group). A single 15-mg dose of upadacitinib extended-release formulation was administered under fasting conditions. Serial plasma and urine samples were assayed to evaluate the effect of renal impairment on upadacitinib exposure through regression analysis and analysis of covariance. The primary analysis was the regression analysis of upadacitinib exposures versus estimated glomerular filtration rate. The point estimates for upadacitinib plasma exposure ratios (90% confidence interval [CI]) in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment were 1.18 (90%CI, 1.06-1.32), 1.33 (90%CI, 1.11-1.59), and 1.44 (90%CI, 1.14-1.82) for area under the plasma concentration-time curve and 1.06 (90%CI, 0.92-1.23), 1.11 (90%CI, 0.88-1.40), and 1.14 (90%CI, 0.84-1.56) for maximum observed plasma concentration, respectively, relative to subjects with normal renal function based on the regression analysis. The analysis of covariance categorical analysis provided consistent results. Upadacitinib was well tolerated by all subjects, and no safety issues were identified in subjects with renal impairment. Renal impairment has a limited effect on upadacitinib pharmacokinetics. This is in agreement with the known limited role of urinary excretion in upadacitinib elimination. Based on the limited impact on exposure, no dose adjustment is necessary for upadacitinib in subjects with impaired renal function.
Keywords: Janus kinase inhibitor; pharmacokinetics; renal impairment; upadacitinib.
© 2019, The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib Using the Immediate-Release and Extended-Release Formulations in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analyses of Phase I-III Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Aug;58(8):1045-1058. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00739-3. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 30945116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib in Healthy Subjects and Subjects With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis, or Atopic Dermatitis: Population Analyses of Phase 1 and 2 Clinical Trials.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;60(4):528-539. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1550. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31701537
-
Characterization of the Effect of Hepatic Impairment on Upadacitinib Pharmacokinetics.J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;59(9):1188-1194. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1414. Epub 2019 Apr 11. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30973649 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analyses of Phase I and II Clinical Trials.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018 Aug;57(8):977-988. doi: 10.1007/s40262-017-0605-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018. PMID: 29076110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical Assessment of Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction Potential of Tofacitinib, Baricitinib and Upadacitinib, the Three Approved Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Drug Saf. 2020 Aug;43(8):711-725. doi: 10.1007/s40264-020-00938-z. Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32367507 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety profile and dose-dependent adverse events of upadacitinib in randomized clinical trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1598972. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1598972. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40626312 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Upadacitinib: Review of Data Relevant to the Rheumatoid Arthritis Indication.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020 May;59(5):531-544. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00855-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31867699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal and Urological Disorders Associated With Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023 Aug 1;29(8):1306-1316. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac140. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023. PMID: 35942657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Nephropathies: Exploring the Gut-Kidney Axis.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;14(12):1541. doi: 10.3390/life14121541. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Safety Warnings on the Prescribing Attitude of JAK Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Italy.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 4;13(13):3929. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133929. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Norman P. Selective JAK inhibitors in development for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014;23(8):1067–1077. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed MF, Camp HS, Jiang P, Padley RJ, Asatryan A, Othman AA. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of ABT‐494, a novel selective JAK 1 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(12):1547–1558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

