YC-1 Prevents Tumor-Associated Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Hypoxic Conditions by Inhibiting p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30634531
- PMCID: PMC6359014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020244
YC-1 Prevents Tumor-Associated Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Hypoxic Conditions by Inhibiting p38/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
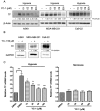
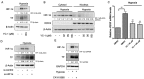
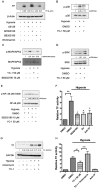
Tissue factor (TF) expressed in cancer cells has been linked to tumor-associated thrombosis, a major cause of mortality in malignancy. Hypoxia is a common feature of solid tumors and can upregulate TF. In this study, the effect of YC-1, a putative inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), on hypoxia-induced TF expression was investigated in human lung cancer A549 cells. YC-1 selectively prevented hypoxia-induced TF expression and procoagulant activity without affecting the basal TF levels. Surprisingly, knockdown or pharmacological inhibition of HIF-1α failed to mimic YC-1's effect on TF expression, suggesting other mechanisms are involved. NF-κB, a transcription factor for TF, and its upstream regulator p38, were activated by hypoxia exposure. Treatment of hypoxic A549 cells with YC-1 prevented the activation of both NF-κB and p38. Inhibition of p38 suppressed hypoxia-activated NF-κB, and inhibited TF expression and activity to similar levels as treatment with an NF-κB inhibitor. Furthermore, stimulation of p38 by anisomycin reversed the effects of YC-1. Taken together, our results suggest that YC-1 prevents hypoxia-induced TF in cancer cells by inhibiting the p38/NF-κB pathway, this is distinct from the conventional anticoagulants that systemically inhibit blood coagulation and may shed new light on approaches to treat tumor-associated thrombosis.
Keywords: MAP kinases; cancer; hypoxia; procoagulant activity; tissue factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YC-1 inhibits HIF-1 expression in prostate cancer cells: contribution of Akt/NF-kappaB signaling to HIF-1alpha accumulation during hypoxia.Oncogene. 2007 Jun 7;26(27):3941-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210169. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17213816
-
Effects of YC-1 on hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in hypoxic human bladder transitional carcinoma cell line T24 cells.Urol Int. 2012;88(1):95-101. doi: 10.1159/000331881. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Urol Int. 2012. PMID: 22041818
-
Propofol selectively inhibits nuclear factor-κB activity by suppressing p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in human EA.hy926 endothelial cells during intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Apr;9(4):1460-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.1946. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24535078
-
Advances in antitumor research of HIF-1α inhibitor YC-1 and its derivatives.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Apr;133:106400. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106400. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36739684 Review.
-
Versatile pharmacological actions of YC-1: anti-platelet to anticancer.Cancer Lett. 2004 Apr 15;207(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.01.005. Cancer Lett. 2004. PMID: 15127725 Review.
Cited by
-
Mucosa‑associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 inhibitor, MI‑2, attenuates non‑small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis by suppressing the JNK/c‑JUN pathway.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 30;28(4):465. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14598. eCollection 2024 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39119234 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Prediction and Risk Assessment of Lung Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Nov 4;13:8317-8327. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S328918. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34764694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (Juglone) Derivatives as Dual Effective Agents Targeting Platelet-Cancer Interplay through Protein Disulfide Isomerase Inhibition.J Med Chem. 2024 Mar 14;67(5):3626-3642. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02107. Epub 2024 Feb 21. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38381886 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandrin B inhibits epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and stemness of large‑cell lung cancer cells and tumorigenesis in xenografts via inhibiting the NF‑κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.Oncol Rep. 2021 Jun;45(6):115. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8066. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Oncol Rep. 2021. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2024 Aug;52(2):102. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8761. PMID: 33907830 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

