Expression, Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 Channels in the Rodent Hippocampus
- PMID: 30634540
- PMCID: PMC6359635
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020246
Expression, Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 Channels in the Rodent Hippocampus
Abstract
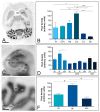
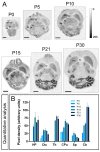
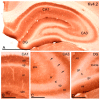
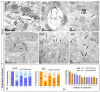
The Kv4 family of voltage-gated K⁺ channels underlie the fast transient (A-type) outward K⁺ current. Although A-type currents are critical to determine somato-dendritic integration in central neurons, relatively little is known about the precise subcellular localisation of the underlying channels in hippocampal circuits. Using histoblot and immunoelectron microscopic techniques, we investigated the expression, regional distribution and subcellular localisation of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in the adult brain, as well as the ontogeny of their expression during postnatal development. Histoblot demonstrated that Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 proteins were widely expressed in the brain, with mostly non-overlapping patterns. During development, levels of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 increased with age but showed marked region- and developmental stage-specific differences. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that labelling for Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 was differentially present in somato-dendritic domains of hippocampal principal cells and interneurons, including the synaptic specialisation. Quantitative analyses indicated that most immunoparticles for Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 were associated with the plasma membrane in dendritic spines and shafts, and that the two channels showed very similar distribution patterns in spines of principal cells and along the surface of granule cells. Our data shed new light on the subcellular localisation of Kv4 channels and provide evidence for their non-uniform distribution over the plasma membrane of hippocampal neurons.
Keywords: electron microscopy; hippocampus; histoblot; immunohistohemistry; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson P., Morris R., Amaral D., Bliss T., O’Kefefe J. The Hippocampus Book. Oxford University Press Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 2007.
-
- MacDonald J.F., Belrose J.C., Xie Y.F., Jackson M.F. Nonselective cation channels and links to hippocampal ischemia, aging, and dementia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013;961:433–447. - PubMed
-
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates Inc.; Sunderland, MA, USA: 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

