Pharmacokinetic Properties of Arsenic Species after Intravenous and Intragastrical Administration of Arsenic Trioxide Solution in Cynomolgus Macaques Using HPLC-ICP-MS
- PMID: 30634677
- PMCID: PMC6359110
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24020241
Pharmacokinetic Properties of Arsenic Species after Intravenous and Intragastrical Administration of Arsenic Trioxide Solution in Cynomolgus Macaques Using HPLC-ICP-MS
Abstract
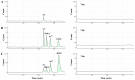
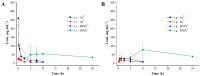
A rapid and sensitive method was established for arsenic (As) speciation based on high performance liquid chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS). This method was validated for the quantification of four arsenic species, including arsenite (AsIII), arsenate (AsV), monomethylarsonic acid (MMAV) and dimethylarsinic acid (DMAV) in cynomolgus macaque plasma. Separation was achieved in just 3.7 min with an alkyl reverse phase column and highly aqueous mobile phase containing 20 mM citric acid and 5 mM sodium hexanesulfonate (pH = 4.3). The calibration curves were linear over the range of 5⁻500 ng·mL-1 (measured as As), with r > 0.99. The above method was validated for selectivity, precision, accuracy, matrix effect, recovery, carryover effect and stability, and applied in a comparative pharmacokinetic study of arsenic species in cynomolgus macaque samples following intravenous and intragastrical administration of arsenic trioxide solution (0.80 mg·kg-1; 0.61 mg·kg-1 of arsenic); in addition, the absolute oral bioavailability of the active ingredient AsIII of arsenic trioxide in cynomolgus macaque samples was derived as 60.9 ± 16.1%.
Keywords: HPLC-ICP-MS; arsenic species; arsenic trioxide; bioavailability; cynomolgus macaque; pharmacokinetic; plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
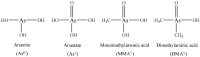
References
-
- Sarquis M. Arsenic and Old Myths. J. Chem. Educ. 1979;56:815–818. doi: 10.1021/ed056p815. - DOI
-
- Kwong Y.L., Todd D. Delicious poison: Arsenic trioxide for the treatment of leukemia [letter] Blood. 1997;89:3487–3488. - PubMed
-
- Shen Z.X., Ni J.H., Li X.S., Xiong S.M., Qiu Q.Y., Zhu J., Tang W., Sun G.L., Yang K.Q., Chen Y., et al. Use of Arsenic Trioxide (As2O3) in the Treatment of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL): II. Clinical Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics in Relapsed Patients. Blood. 1997;89:3354–3360. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Trisenox. [(accessed on 25 September 2010)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2000/21248lbl.pdf.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

