Candida sp. Infections in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 30634716
- PMCID: PMC6352194
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8010076
Candida sp. Infections in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
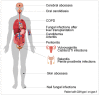
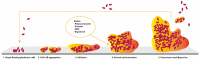
Candidiasis has increased substantially worldwide over recent decades and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, especially among critically ill patients. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder that predisposes individuals to fungal infections, including those related to Candida sp., due to a immunosuppressive effect on the patient. This review aims to discuss the latest studies regarding the occurrence of candidiasis on DM patients and the pathophysiology and etiology associated with these co-morbidities. A comprehensive review of the literature was undertaken. PubMed, Scopus, Elsevier's ScienceDirect, and Springer's SpringerLink databases were searched using well-defined search terms. Predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to classify relevant manuscripts. Results of the review show that DM patients have an increased susceptibility to Candida sp. infections which aggravates in the cases of uncontrolled hyperglycemia. The conclusion is that, for these patients, the hospitalization periods have increased and are commonly associated with the prolonged use of indwelling medical devices, which also increase the costs associated with disease management.
Keywords: Candida; biofilms; candidiasis; diabetes; hyperglycemia; infection; medical devices; metabolic disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention in People at High Risk|NICE Public Health Guideline 38—NICE. [(accessed on 11 September 2018)]; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph38/resources/type-2-diabetes-preventi....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

