T Cells and Regulated Cell Death: Kill or Be Killed
- PMID: 30635093
- PMCID: PMC7325157
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.07.004
T Cells and Regulated Cell Death: Kill or Be Killed
Abstract
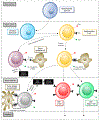
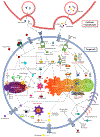
Cell death plays two major complementary roles in T cell biology: mediating the removal of cells that are targeted by T cells and the removal of T cells themselves. T cells serve as major actors in the adaptive immune response and function by selectively killing cells which are infected or dysfunctional. This feature is highly involved during homeostatic maintenance, and is relied upon and modulated in the context of cancer immunotherapy. The vital recognition and elimination of both autoreactive T cells and cells which are unable to recognize threats is a highly selective and regulated process. Moreover, detection of potential threats will result in the activation and expansion of T cells, which on resolution of the immune response will need to be eliminated. The culling of these T cells can be executed via a multitude of cell death pathways which are used in context-specific manners. Failure of these processes may result in an accumulation of misdirected or dysfunctional T cells, leading to complications such as autoimmunity or cancer. This review will focus on the role of cell death regulation in the maintenance of T cell homeostasis, as well as T cell-mediated elimination of infected or dysfunctional cells, and will summarize and discuss the current knowledge of the cellular mechanisms which are implicated in these processes.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer immunotherapy; Cell death; Ferroptosis; Granzymes; Immunosurveillance; Necroptosis; Pyroptosis; T cell.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abdool K, Cretney E, Brooks AD, Kelly JM, Swann J, Shanker A, Bere EW Jr., Yokoyama WM, Ortaldo JR, Smyth MJ, Sayers TJ, 2006. NK cells use NKG2D to recognize a mouse renal cancer (Renca), yet require intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on the tumor cells for optimal perforin-dependent effector function. J Immunol 177, 2575–2583. https://doi.org/177/4/2575 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Afshar-Sterle S, Zotos D, Bernard NJ, Scherger AK, Rödling L, Alsop AE, Walker J, Masson F, Belz GT, Corcoran LM, O’reilly LA, Strasser A, Smyth MJ, Johnstone R, Tarlinton DM, Nutt SL, Kallies A, 2014. Fas ligand-mediated immune surveillance by T cells is essential for the control of spontaneous B cell lymphomas. Nat. Med 20, 283–290. 10.1038/nm.3442 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

