Ameliorative role of antioxidant supplementation on sodium-arsenite induced adverse effects on the developing rat cerebellum
- PMID: 30635247
- PMCID: PMC7772504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2018.02.138
Ameliorative role of antioxidant supplementation on sodium-arsenite induced adverse effects on the developing rat cerebellum
Abstract
Background: Arsenic is an environmental contaminant of global concern. Consumption of ground water contaminated with inorganic arsenic (iAs) continues to be the major source of its exposure. The developing nervous system is especially vulnerable to environmental insults due to its higher rate of oxygen consumption and provision of weaker antioxidant (AOX) machinery.
Objective: Since oxidative stress has been reported as one of the major factors underlying iAs induced toxicity, the aim of the present study is to study the effect of two AOXs i.e., Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) and Curcumin (Cur) in developing cerebellum of rats exposed to arsenic during postnatal period.
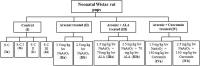
Materials and methods: The study was carried out on mother reared neonatal rat pups grouped as normal (Ia) and sham (vehicle) controls (Ib,c,d), while the experimental groups IIa/ IIb received sodium arsenite (NaAsO2) [(1.5/2.5 mg/kg body weight (bw)] alone or along with ALA (70 mg/kg bw)- IIIa/ IIIb or along with Cur (150 mg/kg bw)- IVa/ IVb. Behavioural, biochemical and immunohistochemical procedures were carried out to understand the underlying mechanisms.
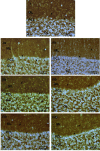
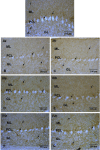
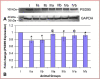
Results: The observations indicated deficits in locomotor function, accumulation of iAs, increased levels of oxidative stress markers along with downregulation of the expression of proteins closely associated with synaptic functioning (Synaptophysin and Postsynaptic density protein95) in the cerebellum of iAs treated animals. Substantial recovery in all these parameters was observed in AOX co-treated groups.
Conclusion: Our results support the potential of ALA and Cur in amelioration of iAs induced developmental neurotoxicity. ALA and Cur can be proposed as dietary adjuvants amongst populations inhabiting areas with high iAs contamination as a safe and cost effective antidotes.
Keywords: PSD95; alpha lipoic acid; curcumin; synaptophysin.
Copyright © 2018 Transdisciplinary University, Bangalore and World Ayurveda Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of α-lipoic acid on spatial memory and structural integrity of developing hippocampal neurons in rats subjected to sodium arsenite exposure.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;75:103323. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2020.103323. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31935550
-
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) modulates expression of apoptosis associated proteins in hippocampus of rats exposed during postnatal period to sodium arsenite (NaAsO2).Toxicol Rep. 2015 Jan 28;2:78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.01.011. eCollection 2015. Toxicol Rep. 2015. PMID: 28962340 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant supplementation upregulates calbindin expression in cerebellar Purkinje cells of rat pups subjected to post natal exposure to sodium arsenite.Brain Res. 2018 Jul 1;1690:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29630858
-
Biomarkers of exposure: a case study with inorganic arsenic.Environ Health Perspect. 2006 Nov;114(11):1790-6. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9058. Environ Health Perspect. 2006. PMID: 17107869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Health Effects and Underlying Biological Mechanisms of Developmental Exposure to Arsenic.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018 Mar;5(1):134-144. doi: 10.1007/s40572-018-0184-1. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018. PMID: 29411302 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-lipoic acid, as an effective agent against toxic elements: a review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3345-3372. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03576-9. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39556148 Review.
References
-
- Dobbing J., Sands J. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum Dev. 1979;3(1):79–83. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. II. Phases in the maturation of Purkinje cells and of the molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972;145(4):399–463. - PubMed
-
- Bouet V., Dijk F., Ijkema-Paassen J., Wubbels R.J., van der Want J.J., Gramsbergen A. Early hypergravity exposure effects calbindin-D28k and inositol-3-phosphate expression in Purkinje cells. Neurosci Lett. 2005;382(1, suppl 2):10–15. - PubMed
-
- Kalia M. Brain development: anatomy, connectivity, adaptive plasticity, and toxicity. Metabolism Suppl. 2008;57(2):S2–S5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

