WNT/β-catenin Pathway Activation Correlates with Immune Exclusion across Human Cancers
- PMID: 30635339
- PMCID: PMC6522301
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1942
WNT/β-catenin Pathway Activation Correlates with Immune Exclusion across Human Cancers
Abstract
Purpose: The T-cell-inflamed phenotype correlates with efficacy of immune-checkpoint blockade, whereas non-T-cell-inflamed tumors infrequently benefit. Tumor-intrinsic WNT/β-catenin signaling mediates immune exclusion in melanoma, but association with the non-T-cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment in other tumor types is not well understood.
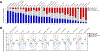
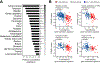
Experimental design: Using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), a T-cell-inflamed gene expression signature segregated samples within tumor types. Activation of WNT/β-catenin signaling was inferred using three approaches: somatic mutations or somatic copy number alterations (SCNA) in β-catenin signaling elements including CTNNB1, APC, APC2, AXIN1, and AXIN2; pathway prediction from RNA-sequencing gene expression; and inverse correlation of β-catenin protein levels with the T-cell-inflamed gene expression signature.
Results: Across TCGA, 3,137/9,244 (33.9%) tumors were non-T-cell-inflamed, whereas 3,161/9,244 (34.2%) were T-cell-inflamed. Non-T-cell-inflamed tumors demonstrated significantly lower expression of T-cell inflammation genes relative to matched normal tissue, arguing for loss of a natural immune phenotype. Mutations of β-catenin signaling molecules in non-T-cell-inflamed tumors were enriched three-fold relative to T-cell-inflamed tumors. Across 31 tumors, 28 (90%) demonstrated activated β-catenin signaling in the non-T-cell-inflamed subset by at least one method. This included target molecule expression from somatic mutations and/or SCNAs of β-catenin signaling elements (19 tumors, 61%), pathway analysis (14 tumors, 45%), and increased β-catenin protein levels (20 tumors, 65%).
Conclusions: Activation of tumor-intrinsic WNT/β-catenin signaling is enriched in non-T-cell-inflamed tumors. These data provide a strong rationale for development of pharmacologic inhibitors of this pathway with the aim of restoring immune cell infiltration and augmenting immunotherapy.See related commentary by Dangaj et al., p. 2943.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: JL: DSMB: TTC Oncology; SAB: 7 Hills, Actym, Alphamab Oncology, Array, BeneVir, Mavu, Tempest; Consultancy: Aduro, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Castle, CheckMate, Compugen, EMD Serono, IDEAYA, Immunocore, Janssen, Jounce, Merck, NewLink, Novartis, RefleXion, Spring Bank, Syndax, Tempest, Vividion, WntRx; Research Support: (clinical trials unless noted) AbbVie, Array (Scientific Research Agreement; SRA), Boston Biomedical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celldex, CheckMate (SRA), Compugen, Corvus, EMD Serono, Evelo (SRA), Delcath, Five Prime, FLX Bio, Genentech, Immunocore, Incyte, Leap, MedImmune, Macrogenics, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Palleon (SRA), Merck, Tesaro, Xencor
Travel: Array, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeneVir, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Castle, CheckMate, EMD Serono, IDEAYA, Immunocore, Janssen, Jounce, Merck, NewLink, Novartis, RefleXion
Patents: (both provisional) Serial #15/612,657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof)
RB declares no disclosures or conflicts of interest
RS has received consulting fees or honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, Puma and has research support from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, MIrati, CytomX.
SS is holding a patent on WNT/b-catenin targeting to enhance anti-tumor immune responses (PCT15/155,099), serves on the SAB on Venn Therapeutics, Tango Therapeutics and consults for TAKEDA, Replimune, Ribon, Torque and Arcus.
T.F.G. has received consultancy fees from Merck, Roche-Genentech, Abbvie, Bayer, Jounce, Aduro, Fog Pharma, Adaptimmune, FivePrime, and Sanofi. T.F.G. has received research support from Roche-Genentech, BMS, Merck, Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Celldex, Ono, Evelo, Bayer, Aduro. T.F.G. has intellectual property/licensing agreements with Aduro, Evelo, and BMS. T.F.G is a co-founder/shareholder with Jounce.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tumor Landscapes: β-Catenin Drives Immune Desertification.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 15;25(10):2943-2945. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0188. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30837277
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

