Conditional Synaptic Vesicle Markers for Drosophila
- PMID: 30635441
- PMCID: PMC6404611
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.118.200975
Conditional Synaptic Vesicle Markers for Drosophila
Abstract
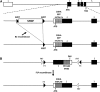
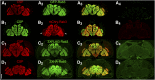
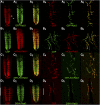
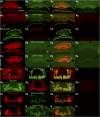
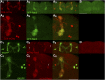
The release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles (SVs) at pre-synaptic release sites is the principle means by which information transfer between neurons occurs. Knowledge of the location of SVs within a neuron can thus provide valuable clues about the location of neurotransmitter release within a neuron and the downstream neurons to which a given neuron is connected, important information for understanding how neural circuits generate behavior. Here the development and characterization of four conditional tagged SV markers for Drosophila melanogaster is presented. This characterization includes evaluation of conditionality, specificity for SV localization, and sensitivity of detection in diverse neuron subtypes. These four SV markers are genome-edited variants of the synaptic vesicle-specific protein Rab3. They depend on either the B2 or FLP recombinases for conditionality, and incorporate GFP or mCherry fluorescent proteins, or FLAG or HA epitope tags, for detection.
Keywords: Drosophila; conditional; epitope; fluorescent; synaptic vesicle.
Copyright © 2019 Williams et al.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
