Sphenopalatine ganglion block for treatment of post-dural puncture headache in obstetric patients: An observational study
- PMID: 30636799
- PMCID: PMC6299770
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_443_18
Sphenopalatine ganglion block for treatment of post-dural puncture headache in obstetric patients: An observational study
Abstract
Background and aims: Post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) is a consequence of spinal and epidural anaesthesia in approximately 1% of obstetric patients. The gold standard for its treatment is epidural blood patch. Sphenopalatine ganglion block (SPGB) has been proposed as a non-invasive intervention with minimal adverse effect. The primary objective of this study was to assess the efficacy of SPGB for treatment of PDPH. Secondary objectives were to assess onset of analgesia, duration of block and adverse effects.
Methods: Twenty parturients diagnosed to have PDPH, resistant to standard treatment modalities such as intravenous fluids, abdominal binder, bed rest and caffeine, were recruited into this prospective observational study. Patients were allocated to either of the two groups. Group A patients received paracetamol 1 g 8 hourly intravenously for a day. If adequate pain relief was not achieved, diclofenac 75 mg 12 hourly was added. Patients in group B received SPGB with 2% lignocaine. Fisher's exact test, Mann-Whitney test and independent sample t-test were used for statistical analysis.
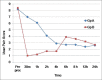
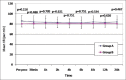
Results: About 88.89% patients in group B had adequate pain relief within 5 min of block (P < 0.001). Pain was significantly lower in Group B for up to 8 h, with no adverse effects.
Conclusion: SPGB is an effective initial modality for managing severe headache in patients with PDPH.
Keywords: Analgesia; obstetric; post-dural puncture headache; sphenopalatine ganglion block; spinal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Atim A, Ergin A, Yanarates O, Kuyumcu M, Kurt E. Epidural blood patch for the management of post-dural puncture headache. J Nervous Sys Surgery. 2009;2:67–71.
-
- Davies JM, Murphy A, Sullivan GO, Smith M. Subdural hematoma after dural puncture headache treated by epidural blood patch. Br J Anaesth. 2001;86:720–3. - PubMed
-
- Desai MJ, Dave AP, Martin MB. Delayed radicular pain following two large volume epidural blood patches for post-lumbar puncture headache: A case report. Pain Physician. 2010;13:257–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources