Erectile Dysfunction in 45-Year-Old Heterosexual German Men and Associated Lifestyle Risk Factors and Comorbidities: Results From the German Male Sex Study
- PMID: 30638828
- PMCID: PMC6377383
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esxm.2018.11.004
Erectile Dysfunction in 45-Year-Old Heterosexual German Men and Associated Lifestyle Risk Factors and Comorbidities: Results From the German Male Sex Study
Abstract
Background: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common public health issue with a significant impact on quality of life. The associations between ED and several risk factors have been reported previously. The continuously increasing incidence of these factors is contributing to the increasing prevalence of ED.
Aim: To assess ED prevalence and severity in a representative sample of 45-year-old German men and to analyze the association with risk factors (lifestyle risk factors/comorbidities).
Methods: Data were collected within the German Male Sex-Study. Randomly selected 45-year-old men were invited. A total of 10,135 Caucasian, heterosexual, sexually active men were included in this analysis. The self-reported prevalence of ED was assessed using the Erectile Function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function. Risk factors for ED were ascertained using self-report questionnaires. An anamnesis interview and a short physical examination were performed.
Main outcome measure: ED prevalence and severity were evaluated in a cross-sectional design. The associations of ED with comorbidities (eg, depression, diabetes, hypertension, lower urinary tract symptoms) and lifestyle factors (ie, smoking, obesity, central obesity, physical inactivity, and poor self-perceived health-status) were analyzed by logistic regression.
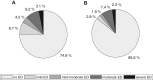
Results: The overall prevalence of ED was 25.2% (severe, 3.1%; moderate, 9.2%; mild to moderate, 4.2%; mild, 8.7%). Among the men with ED, 48.8% had moderate or severe symptoms. ED prevalence increased with the number of risk factors, to as high as 68.7% in men with 5-8 risk factors. In multiple logistic regression with backward elimination, the strongest associations with ED were found for depression (odds ratio [OR] = 1.87), poor self-perceived health status (OR = 1.72), lower urinary tract symptoms (OR = 1.68), and diabetes (OR = 1.38).
Conclusion: One out of 4 men already had symptoms of ED at age 45. Almost one-half of the men with ED had moderate to severe symptoms. ED was strongly associated with each analyzed risk factor, and the prevalence and severity of ED increased with an increasing number of risk factors. Hallanzy J, Kron M, Goethe VE, et al. Erectile Dysfunction in 45-Year-Old Heterosexual German Men and Associated Lifestyle Risk Factors and Comorbidities: Results From the German Male Sex Study. Sex Med 2019;7:26-34.
Keywords: Erectile Dysfunction; German Male Sex-Study; Middle-Aged Men; Prevalence; Risk Factors; Severity.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Re: Erectile Dysfunction in 45-Year-Old Heterosexual German Men and Associated Lifestyle Risk Factors and Comorbidities: Results from the German Male Sex Study.J Urol. 2019 Oct;202(4):644. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000576956.80316.36. Epub 2019 Sep 6. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31287750 No abstract available.
References
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H.A., Goldstein I., Hatzichristou D.G. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: Results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Rosen R.C., Fisher W.A., Eardley I. The multinational Men's Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study: I. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and related health concerns in the general population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004;20:607–617. - PubMed
-
- Braun M., Wassmer G., Klotz T. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: Results of the Cologne Male Survey. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:305–311. - PubMed
-
- McCabe M.P., Sharlip I.D., Lewis R. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: A consensus statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144–152. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

