PYY plays a key role in the resolution of diabetes following bariatric surgery in humans
- PMID: 30639417
- PMCID: PMC6413583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.040
PYY plays a key role in the resolution of diabetes following bariatric surgery in humans
Abstract
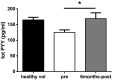
Background: Bariatric surgery leads to early and long-lasting remission of type 2 diabetes (T2D). However, the mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain unclear. Among several factors, gut hormones are thought to be crucial mediators of this effect. Unlike GLP-1, the role of the hormone peptide tyrosine tyrosine (PYY) in bariatric surgery in humans has been limited to appetite regulation and its impact on pancreatic islet secretory function and glucose metabolism remains under-studied.
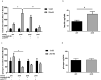
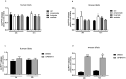
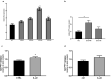
Methods: Changes in PYY concentrations were examined in obese patients after bariatric surgery and compared to healthy controls. Human pancreatic islet function was tested upon treatment with sera from patients before and after the surgery, in presence or absence of PYY. Alterations in intra-islet PYY release and insulin secretion were analysed after stimulation with short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acids and the cytokine IL-22.
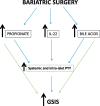
Findings: We demonstrate that PYY is a key effector of the early recovery of impaired glucose-mediated insulin and glucagon secretion in bariatric surgery. We establish that the short chain fatty acid propionate and bile acids, which are elevated after surgery, can trigger PYY release not only from enteroendocrine cells but also from human pancreatic islets. In addition, we identify IL-22 as a new factor which is modulated by bariatric surgery in humans and which directly regulates PYY expression and release.
Interpretation: This study shows that some major metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery can be emulated ex vivo. Our findings are expected to have a direct impact on the development of new non-surgical therapy for T2D correction.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Diabetes; Gut hormones; IL-22; PYY; Pancreatic hormone secretion.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Dempster reports grants from the University of Oxford Novo Nordisk Clinical Research Fellowship, during the conduct of the study. Dr. Larraufie reports grants from Wellcome trust and UK government (MRC), during the conduct of the study. Dr. Gribble reports grants from Wellcome Trust and UK Government (MRC), during the conduct of the study; grants from MedImmune, grants from Wellcome Trust, grants from UK government (MRC and BBSRC), personal fees from Kallyope (New York), outside the submitted work; Dr. Reimann reports grants from Wellcome Trust and UK Government (MRC), during the conduct of the study; grants from MedImmune, grants from Wellcome Trust, grants from UK government (MRC and BBSRC), outside the submitted work. Dr. Cobbold reports personal fees from NovoNordisk, personal fees from Intercept, outside the submitted work. Dr. Pavlides reports other from Oxford NIHR Biomedical Research Centre, during the conduct of the study; other from Perspectum Diagnostics, outside the submitted work. All the other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Buchwald H., Estok R., Fahrbach K., Banel D., Jensen M.D., Pories W.J. Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2009;122(3):248–256. e5. - PubMed
-
- Holst J.J., Madsbad S. Mechanisms of surgical control of type 2 diabetes: GLP-1 is key factor. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(6):1236–1242. - PubMed
-
- Pournaras D.J., Osborne A., Hawkins S.C., Mahon D., Ghatei M.A., Bloom S.R. The gut hormone response following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: cross-sectional and prospective study. Obes Surg. 2010;20(1):56–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

