Developmental trajectories of autonomic functioning in autism from birth to early childhood
- PMID: 30641105
- PMCID: PMC6401242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2019.01.003
Developmental trajectories of autonomic functioning in autism from birth to early childhood
Abstract
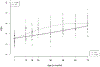
Deficits in social engagement emerge in autism during the infant and toddler period and may be related to emotion regulation and stress response systems. This study examined patterns of growth in autonomic functioning related to autism diagnosis and addresses the hypothesis that there are differences in autonomic functioning related to autism in infancy. Heart rate (HR) and respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) were measured at 8 time points from 1 to 72 months of age in infants later diagnosed with autism (n = 12) and a non-autistic comparison group (n = 106). Multilevel models were used to describe the developmental course of HR and RSA and to test the effect of autism diagnosis on growth trajectories. Both groups showed an expected age-related decrease in HR and increase in RSA. Groups did not differ in the rate of decrease of HR over time. However, infants with autism demonstrated a smaller linear increase in RSA, indicating slower growth in RSA over time in comparison to controls. These results suggest that differences in physiological regulation may develop with age in autism. The slowed RSA growth in autism was most evident after 18 months of age, at a time when behavioral symptoms become prominent. This is consistent with the view that RSA is a marker of functional status in autism rather than a cause of social deficits in autism.
Keywords: Autism; Cardiac; Infancy; Longitudinal; Physiology.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bayley N (1993). Bayley Scales of Infant Development, Second Edition San Antonio: Psychological Corporation.
-
- Beauchaine T (2001). Vagal tone, development, and Gray’s motivational theory: Toward an integrated model of autonomic nervous system functioning in psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol, 13(2), 183–214. - PubMed
-
- Berntson GG, Bigger JT, Eckberg DL, Grossman P, Kaufmann PG, Malik M, … Van der Molen MW (1997). Heart rate variability: Origins, methods, and interpretive caveats. Psychophysiology, 34, 623–648. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein MH, & Suess PE (2000). Child and mother cardiac vagal tone: Continuity, stability, and concordance across the first 5 years. Dev Psychol, 36(1), 54–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources