Iron as a Central Player and Promising Target in Cancer Progression
- PMID: 30641920
- PMCID: PMC6359419
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20020273
Iron as a Central Player and Promising Target in Cancer Progression
Abstract
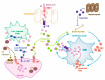
Iron is an essential element for virtually all organisms. On the one hand, it facilitates cell proliferation and growth. On the other hand, iron may be detrimental due to its redox abilities, thereby contributing to free radical formation, which in turn may provoke oxidative stress and DNA damage. Iron also plays a crucial role in tumor progression and metastasis due to its major function in tumor cell survival and reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, pathways of iron acquisition, export, and storage are often perturbed in cancers, suggesting that targeting iron metabolic pathways might represent opportunities towards innovative approaches in cancer treatment. Recent evidence points to a crucial role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) as a source of iron within the tumor microenvironment, implying that specifically targeting the TAM iron pool might add to the efficacy of tumor therapy. Here, we provide a brief summary of tumor cell iron metabolism and updated molecular mechanisms that regulate cellular and systemic iron homeostasis with regard to the development of cancer. Since iron adds to shaping major hallmarks of cancer, we emphasize innovative therapeutic strategies to address the iron pool of tumor cells or cells of the tumor microenvironment for the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: iron chelators; iron homeostasis; lipocalin-2; macrophage polarization; tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Inoue S., Kawanishi S. Hydroxyl radical production and human DNA damage induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate and hydrogen peroxide. Cancer Res. 1987;47:6522–6527. - PubMed
-
- Thanan R., Oikawa S., Yongvanit P., Hiraku Y., Ma N., Pinlaor S., Pairojkul C., Wongkham C., Sripa B., Khuntikeo N., et al. Inflammation-induced protein carbonylation contributes to poor prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012;52:1465–1472. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

