Dopamine/2-Phenylethylamine Sensitivity of Ion-Selective Electrodes Based on Bifunctional-Symmetrical Boron Receptors
- PMID: 30642018
- PMCID: PMC6358993
- DOI: 10.3390/s19020283
Dopamine/2-Phenylethylamine Sensitivity of Ion-Selective Electrodes Based on Bifunctional-Symmetrical Boron Receptors
Abstract
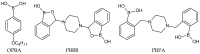
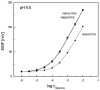
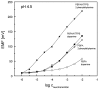
Piperazine-based compounds bearing two phenylboronic acid or two benzoxaborole groups (PBPA and PBBB) were applied as dopamine receptors in polymeric membranes (PVC/DOS) of ion-selective electrodes. The potentiometric sensitivity and selectivity of the sensors towards dopamine were evaluated and compared with the results obtained for 2-phenylethylamine. Since the developed electrodes displayed strong interference from 2-phenylethylamine, single-molecule geometry optimizations were performed using the density functional theory (DFT) method in order to investigate the origin of dopamine/2-phenylethylamine selectivity. The results indicated that phenylboronic acid and benzoxaborole receptors bind dopamine mainly through the dative B⁻N bond (like 2-phenylethylamine) and the potentiometric selectivity is mainly governed by the higher lipophilicity of 2-phenylethylamine.
Keywords: dopamine; ion-selective electrodes; organoboron receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Miyaura N., Suzuki A. Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. Chem. Rev. 1995;95:2457–2483. doi: 10.1021/cr00039a007. - DOI
-
- Ferrier R.J. Carbohydrate boronates. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1978;35:31–80.
-
- Yu H., Wang B. Phenylboronic acids facilitated selective reduction of aldehydes by tributyltin hydride. Synth. Commun. 2001;31:163–169. doi: 10.1081/SCC-100105400. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

