Polymer Optical Fiber Tip Mass Production Etch Mechanism to Achieve CPC Shape for Improved Biosensor Performance
- PMID: 30642022
- PMCID: PMC6359282
- DOI: 10.3390/s19020285
Polymer Optical Fiber Tip Mass Production Etch Mechanism to Achieve CPC Shape for Improved Biosensor Performance
Abstract
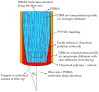
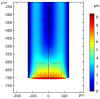
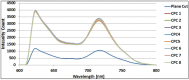
We report on a simple chemical etching method that enables nonlinear tapering of Polymer Optical Fiber (POF) tips to manufacture Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) fiber tips. We show that, counter-intuitively, nonlinear tapering can be achieved by first etching the core and not the cladding. The etching mechanism is modelled and etched tips are characterized both geometrically and optically in a fluorescence glucose sensor chemistry. A Zemax model of the CPC tipped sensor predicts an optimal improvement in light capturing efficiency of a factor of 3.96 compared to the conventional sensor with a plane-cut fiber tip. A batch of eight CPC fiber tips has been manufactured by the chemical etching method. The batch average showed an increase of a factor of 3.16, which is only 20% less than the predicted value. The method is reproducible and can be up-scaled for mass production.
Keywords: blood or tissue constituent monitoring; etching; fiber optic sensors; nonimaging optics; polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Polymer optical fiber compound parabolic concentrator tip for enhanced coupling efficiency for fluorescence based glucose sensors.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 Nov 20;6(12):5008-20. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.005008. eCollection 2015 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26713213 Free PMC article.
-
Femtosecond laser micromachining of compound parabolic concentrator fiber tipped glucose sensors.J Biomed Opt. 2017 Mar 1;22(3):37003. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.22.3.037003. J Biomed Opt. 2017. PMID: 28290597
-
Single fiber-optic pH sensor based on changes in reflection accompanying polymer swelling.Anal Chem. 1994 May 15;66(10):1731-5. doi: 10.1021/ac00082a021. Anal Chem. 1994. PMID: 8030785
-
Towards a Uniform Metrological Assessment of Grating-Based Optical Fiber Sensors: From Refractometers to Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2017 Jun 21;7(2):23. doi: 10.3390/bios7020023. Biosensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28635665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical fiber biochemical sensors for continuous monitoring.Med Des Mater. 1991 Apr;1(4):24-30. Med Des Mater. 1991. PMID: 10183945 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Integration of Optical Fibers and Nanomaterials for Aircraft Systems.Materials (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;16(4):1433. doi: 10.3390/ma16041433. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36837063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annular Cavity Design for Photoluminescent Polymer Optical Fiber Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 11;20(18):5199. doi: 10.3390/s20185199. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32933092 Free PMC article.
-
Cortisol Monitoring Devices toward Implementation for Clinically Relevant Biosensing In Vivo.Molecules. 2023 Mar 3;28(5):2353. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052353. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zubia J., Arrue J. Plastic optical fibers: An introduction to their technological processes and applications. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2001;7:101–140. doi: 10.1006/ofte.2000.0355. - DOI
-
- Marques C.A.F., Webb D.J., Andre P. Polymer optical fiber sensors in human life safety. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017;36:144–154. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2017.03.010. - DOI
-
- Hassan H.U., Janting J., Aasmul S., Bang O. Polymer Optical Fiber Compound Parabolic Concentrator Fiber Tip-Based Glucose Sensor: In Vitro Testing. IEEE Sens. J. 2016;16:84838488. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2606580. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

